"Geriforte 100 mg with visa, herbals that increase bleeding".
By: H. Trompok, M.S., Ph.D.
Program Director, Loma Linda University School of Medicine
Purchase genuine geriforte on line
Tears have been implicated as internal derangements that may cause restriction, clicking, and sometimes painful limitation of arm movement. Tears may also occur with sudden or excessive biceps contraction on the upper part of the labrum where the biceps tendon inserts. Rotator cuff tendonosis/tear: the rotator cuff consists of the supraspinatus, infraspinatus, subscapularis, and teres minor muscles which originate on the scapula and whose tendons insert on the humerus. When damaged by sudden trauma, overuse, or overexertion, fibers of the tendon become sprained and inflamed. Partial supraspinatus tears are the most common and may occur on the bursal side or the articular side of the tendon. Differential Diagnosis and Management for the Chiropractor – Protocols and Algorithms. From behind Painful Arc test – Active abduction from hand at side to hand over head is pain patient stabilize scapula with one hand and humeral head with other. Pain in midrange by poster to anterior pressure toward glenoid to test anterior stability; pull backward is positive. Provide resistance against further shoulder flexion and evaluate for Neer’s test – assesses for possible rotator cuff impingement. If pain was present with the thumb down but relieved with the thumb up, it is considered a scapula (place your hand firmly upon the acromion, or hold the inferior angle of positive test, suspicious for a labral tear. Stabilize the of the humerous with a posterior force to see if the pain and or sense of apprehension is relieved. Rotator Cuff Tears Yergason’ s test – Flex elbow to 90°, shake hands with patient and provide Abduction test – Active abduction to 90° while providing resistance proximal to resistance against supination. Pain indicates possible bicipital tendinopathy or a the elbow (primary abductor: supraspinatus). Instruct the patient to externally rotate the shoulder while you provide resistance. Compare the strength of the involved shoulder Type I: Sprain of the acromioclavicular or coracoclavicular ligament. A positive test consists of pain or weakness on Type V: Gross disparity between the acromion and clavicle, which displaces resisting downward pressure on the arms or an inability to perform the tests. Acromioclavicular Joint Crossed Arm Adduction test – Flex the shoulder to 90° and adduct arm across body (reaching for opposite shoulder). Additional Resources for Clinical Examination of Shoulders Labral Tears, Tendon Disorders, Dislocations Apprehension test – Evaluates for anterior glenohumeral stability. Differential Diagnosis and Management for the Chiropractor – Protocols and patient supine, abduct shoulder to 90° and externally rotate arm to place stress Algorithms. If the patient feels apprehension that the arm may dislocate anteriorly, the test is positive. Typically of high quality as Conservative musculoskeletal care is typically care of first resort based on long standing randomization assures similarities of subjects within treatment groups. Typically ‘low tech,’ low cost, with minimal and rare side effects, it is frequently delivered in primary care settings, and by various health providers.
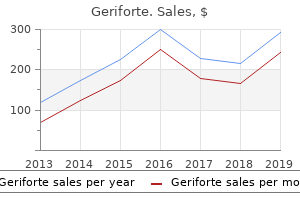
Discount geriforte online amex
Inferior longitudinal Odontoid to body of axis Secondary stabilizer Alar Odontoid to occipital condyles Strong, stabilizing ligaments, limit rotation & lateral bending. Intervertebral disc To adjacent vertebral bodies Annulus gives strong connection b/w adjacent bodies Anterior longitudinal Adjacent anterior vertebral bodies Strong, thick ligament. Continuation of supraspinous ligament arch & C2-C6 spinous processes Supraspinous Dorsal spinous processes to C7 Strong. Osteophytes, discs, facet hypertrophy, and ligamentum flavum can all narow foramen. Occurrence Night pain Infection, tumor With activity Usually mechanical etiology d. Neurologic Pain, numbness, tingling Radiculopathy, neuropathy, cauda equina syndrome symptoms Spasticity, clumsiness Myelopathy Bowel/bladder symptoms Cauda equina syndrome 6. No pressure then raises one leg indicates lack of effort, not true weakness Waddell signs Presence indicates nonorganic pathology: 1. Spinal sensory (dorsal root) ganglion White and gray rami communicantes to and from sympathetic trunk Ventral ramus of spinal n. In lumbar spine the traversing nerve is usually affected, and exiting root is not (except in far lateral compression). Dorsal rami innervate local structures (neck and back musculature, overlying skin, facet capsules, etc). S3 Autonomous S5 L2 sensory zones Co There is actually considerable overlap between L3 L3 L1 any two adjacent S2 S1 dermatomes. Both types of arteries run along roots, but Lateral (or medial) radicular arteries end before sacral arteries reaching anterior or posterior Sacrum spinal arteries; larger segmental medullary arteries continue on to supply a segment of these arteries. Lateral radiograph reveals similar changes Degenerative Disc Disease Radiograph of thoracic spine Degeneration of lumbar intervertebral discs and shows narrowing of interverte hypertrophic changes at vertebral margins with bral spaces and spur formation spur formation. On lateral radiograph, dog appears to be wearing a collar Isthmic type spondylolisthesis. Both between ligaments; coroid acromioclavicular joint; therefore no displacement. Gradual traction overcomes muscle spasm and in most cases achieves reduction in 20–25 minutes. Milch maneuver Patient supine; steady downward traction applied at elbow, combined with slow, gradual external rotation and abduction of limb. Examiner places sole of foot (shoe removed) against patient’s axillary fold for countertraction, grasps patient’s wrist with both hands, and applies steady longitudinal traction. Anatomic neck Neer four-part classification of Greater fractures of proximal humerus. Static: glenoid, labrum, articular congruity, glenohumeral ligaments & capsule, negative intraarticular pressure Dynamic: rotator cuff muscles/tendons, biceps tendon, scapular stabilizers (periscapular muscles), proprioception.
Geriforte 100 mg with visa
Scandinavian Journal of W ork, Environment and Health, Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research, 244: 48–59. Indications for manipulation and corticosteroids Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research, 244: 7–16. The effect of magnetic resonance imaging on Scandinavian Journal of Rheumatology, 4: 193–196. Fractures of the greater tuberosity Shibata Y, M idorikawa K, Emoto G, Naito M (2001). Clinical evalua presenting as rotator cuff abnorm ality: m agnetic resonance tion of sodium hyaluronate for the treatment of patients with demonstration. Goniometric reliability random ized, parallel-group study of the efficacy and safety in a clinical setting: shoulder measurements. Physical Therapy, 67: of proglumetacin and naproxen in periarthritis of the shoulder or 668–673. Current Therapeutic Research, Clinical and Experimental, Rissen D, M elin B, Sandsjo L, Dohns I, Lundberg U (2000). M agnetic resonance imaging of the nolone acetonide injections on hem iplegic shoulder pain: shoulder. Can history and physical examination be used Physiotherapy for patients with soft tissue shoulder disorders: as markers of quality? An analysis of the initial visit note in a systematic review of randomised clinical trials. Extracorporeal shock-wave therapy for pain: more pain is associated with psychological distress and tendonitis of the rotator cuff. Effectiveness of corticosteroid injections traumatic instability of the shoulder: a prospective, randomized versus physiotherapy for treatm ent of painful stiff shoulder multicenter study. Role of shoulder sion of cytokines and nitric oxide synthase isoforms in human ultrasonography in the evaluation of the painful shoulder. Annals of the Rheum atic Diseases, 60: European Journal of Radiology, 19: 142–146. A comparison of ultrasonographic and arthroscopic findings in Archives of Physical M edicine and Rehabilitation, 76: 239–242. Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery, Vidal L, Kneer W, Baturone M, Sigmund R (2001). Sonographic differences in the appearance of acute and Viikari-Juntura E, Takala E, Riihimaki H, M artikainen R, Jappinen P chronic full-thickness rotator cuff tears.

Purchase geriforte 100mg with amex
The term patient has been used throughout the document in preference to other terms such as client or service user. Several professional titles are used by those who practice ultrasound and this can lead to considerable confusion. The term ultrasound practitioner is used throughout this document when appropriate to do so. The definition of ultrasound practitioner within the Glossary section of the above document is: ‘A healthcare professional who holds recognised qualifications in medical ultrasound and is able to competently perform ultrasound examinations falling within their personal scope of practice. The professional background of ultrasound practitioners can be very varied and will include radiologists, radiographers, sonographers, midwives, physiotherapists, obstetricians and clinical scientists’. These Guidelines will be of relevance to all, hence the use of the term ‘ultrasound practitioner’ whenever possible. It does not imply that they hold recognised ultrasound qualifications as would an ultrasound practitioner’. It is the nature of any document whether published in a traditional format or on-line that it can very quickly become out of date. At the time of publication (December 2015), all hyperlinks have been checked and are complete. We would also like to again take this opportunity thank all the contributors and editors of previous editions of the Guidelines who have provided us with such a firm foundation on which to build. Sonographers are qualified healthcare professionals who undertake, report and take responsibility for the conduct of diagnostic, screening and interventional ultrasound examinations. Sonographers also perform advanced diagnostic and therapeutic ultrasound procedures such as biopsies and joint injections. The following definition of ‘sonographer’ is used in connection with the Public Voluntary Register of Sonographers: ‘A healthcare professional who undertakes and reports diagnostic, screening or interventional ultrasound examinations. They are either not medically qualified or hold medical qualifications but are not statutorily registered with the General Medical Council. Individuals without a recognised qualification, including student sonographers should always be supervised by qualified staff. A sonographer should: i) recognise and work within their personal scope of practice, seeking advice as necessary; ii) ensure that a locally agreed and written scheme of work is in place; iii) work with reference to national and local practice and guideline recommendations; iv) ensure they hold appropriate professional indemnity insurance or obtain this by virtue of their employment (ref: section 1. The general standards of education and training for ultrasound practitioners are set out on page 12 of the 2014 Royal College of Radiologists/Society and College of Radiographers document ‘Standards for the Provision of an Ultrasound Service’. The registration situation for sonographers is complex 1 the majority of sonographers are statutorily registered but this will depend on their professional background and is not achievable for all. Government policy since 2011 has been not to bring further aspirant groups into statutory registration unless there is a clear evidence of clinical risk that requires this. Autonomy and accountability for healthcare workers, social care workers and social care workers. The majority of statutorily registered ultrasound practitioners will already meet this requirement and will not need to take any further action. They will either work in an employed environment where their employer will indemnify them, and / or if they undertake self-employed work, they will have already made their own professional indemnity arrangements.
Order 100mg geriforte amex
True contraindications to vaccination: Anaphylactic reaction to a previous dose of the vaccine or: Anaphylaxis to baker’s yeast is a contraindication to HepB vaccine. Specific reactions within 48 hr of vaccine of a previous vaccine: Severe, inconsolable screaming for 3 hr Distinctive high-pitched cry Hyporesponsive episode Temperature >40. Caution should be used when considering these vaccines for healthy individuals in close contact with the immunocompromised. Recent administration of immune globulin may lessen the efficacy of vaccinations Vaccines may be given with the following: Mild acute illness with or without fever Mild to moderate local reaction. Treatment of potential exposure to infectious disease or contaminated wounds follows specific guidelines for active or passive immunization. Treatment of adverse reactions depend on symptoms: Local reactions at the injection site can be treated with cold compresses, analgesics, or antipruritics. Treat fever, headaches, myalgias, and arthralgias with acetaminophen or ibuprofen. Treat ongoing seizures with benzodiazepines Consider prophylaxis with acetaminophen at the time of injection of vaccines and again 4–8 hr later: Children who receive varicella vaccine should avoid salicylates for 6 wk post vaccination because of the association of varicella infection and salicylates to Reye syndrome. Specific discussion with the parents is required to review the risks and benefits of tetanus vaccination, particularly given the frequent occurrence of trauma and the need to provide both passive and active immunity at that time: Document in the chart that the risks and benefits have been thoroughly discussed. The National Childhood Vaccine Injury Act requires that a copy of the Vaccine Information Statements be provided before administering each dose of the vaccine. Unexpected adverse events should be reported to the Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System. Discharge Criteria Patients may be discharged home after routine immunizations unless an immediate adverse reaction occurs. It is essential that follow-up with the primary care physician be arranged to complete immunizations. Clinical practice guideline for the use of antimicrobial agents in neutropenic patients with cancer: 2010 update by the infectious diseases society of america. Perspectives for the management of febrile neutropenic patients with cancer in the 21st century. Efficacy and safety of retapamulin ointment as treatment of impetigo: Randomized double-blind multicentre placebo-controlled trial. For fluid boluses, use normal saline and avoid lactated Ringer and avoid hypotonic fluid. Treat severe hyperammonemia (≥500–600 mmol/L) with immediate dialysis or with ammonia-trapping drugs such as: Arginine hydrochloride Sodium benzoate Sodium phenylacetate Sodium phenylbutyrate Doses vary with disease; consult metabolic physician before use. Consult metabolic physician when any child presents with suspected inherited metabolic disease. Bimodal age distribution, with early peak between teens and early 30s and 2nd peak about age 60 yr. Multifactorial origin involving interplay among the following factors: Genetic Environmental Immune Pathogenesis: Gut wall becomes unable to downregulate its immune responses, ultimately resulting in chronic inflammation. Renal: Nephrolithiasis Obstructive hydronephrosis Musculoskeletal: Peripheral arthritis/arthralgias—follows disease activity.
Purchase genuine geriforte on line. БЮДЖЕТНЫЙ уход от компании Весна.