"Buy brahmi 60caps low price, medications 2015".
By: J. Ateras, M.B. B.CH., M.B.B.Ch., Ph.D.
Vice Chair, Pacific Northwest University of Health Sciences
Buy generic brahmi 60 caps line
These different responses between insulins are likely due to the effect of exercise on the time-action profile of the basal insulin. Interestingly, it has been shown that cycling for 30 minutes at 65% V 0 2max did not influence the absorption rate of insulin glargine and similar declines in blood glucose and insulin were demonstrated compared to a resting control trial (209). The results from this study showed that a 75% reduction in rapid acting insulin was most effective at preserving blood glucose during and after exercise, and preventing hypoglycaemia when exercising at 50% V 0 2max for an hour and 75% V 02max for 30 minutes. Recent findings demonstrated that large post-exercise bolus insulin dose reductions of ~50% may reduce early (<8 hours post-exercise) but not late post-exercise hypoglycaemia following performance of morning steady state continuous exercise (45 minutes running at ~75%V02peak (210). Non-Pharmacological Approach To Prevent Exercise-Induced Hypoglycaemia the manipulation of exercise intensity has great utility in reducing the threat of hypoglycaemia that is imposed by exercise. In these studies, the short duration sprint resulted in greater increases in counterregulatory hormone levels and circulating lactate, but it is unclear why there was a lesser decline in glucose during the early post-exercise recovery period after the addition of the sprint, since no differences in glucose infusion rate or glucose uptake were detected relative to a control trial in which only moderate intensity exercise was performed (215). It was also demonstrated that the performance of this 10 second maximal sprint after moderate intensity exercise might not offer protection against the late-onset of post-exercise hypoglycaemia (215). This conclusion was drawn from the finding that the addition of the sprint to 20 minutes of steady state exercise neither increased nor decreased the amount of glucose required to maintain euglycaemia throughout 8 hours of recovery from exercise, and the sprint had no effect on endogenous glucose production or uptake during this time. Consequently, energy production during high intensity exercise is derived largely from non-oxidative metabolism. This type of exercise is not limited to running, swimming and cycling, but exercise cannot be maintained for a long duration and is therefore generally identified as sprint activities. Interestingly, the cause of this exercise-induced hyperglycaemia appears to differ between different durations of high-intensity exercise. The primary reason for the exercise-induced rise in blood glucose in response to sustained high-intensity exercise, was that exercise elicited a lesser 33 increment in glucose uptake (~4-fold) than the ^7-fold increase in hepatic glucose production (216; 217). In response to high-intensity exercise, more concentrated levels of growth hormone and catecholamines appear within the circulation (10 to 14 fold increase in adrenaline and a 10 to 18 fold increase in noradrenaline) when compared to low and moderate intensity exercise, but a slight increase or no change in glucagon concentrations has been demonstrated (216; 217; 221). In fact, research suggests strong increments in glucose production during high intensity exercise occurs irrespective of circulating insulin levels (222; 223), and catecholamines have an inhibitory effect on insulin-mediated glucose uptake (220). In contrast with low and moderate intensity exercise, insulin levels in those without diabetes might slightly decline (224), but generally remain unchanged during high-intensity exercise (191), irrespective of an exercise-induced increase in blood glucose. This format is typically seen in games activities where athletes are continually moving at a low to moderate intensity but exercise is interspersed with bursts of high-intensity movements. Furthermore, post-exercise blood glucose is better preserved, and the occurrence of early, but not late, post-exercise hypoglycaemia is reduced (but not prevented) by substituting intermittent exercise for a session of moderate intensity continuous exercise (227; 230). The lesser decline in glycaemia during this intermittent exercise session was attributed to a greater increment in the appearance of glucose but an attenuation of glucose uptake during exercise and recovery, and authors suggested that this was related to elevated appearance of counterregulatory hormones, when compared to the moderate intensity exercise session (231).
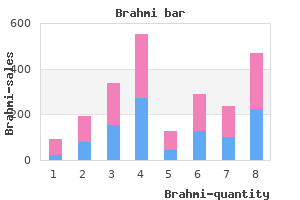
Generic 60caps brahmi visa
It is common practice to provide prophylaxis with mial pneumonias because it does not affect stomach pH H2-receptor antagonists or sucralfate for stress-related and is less likely to permit colonization of the gastroinulcers. In patients more severe degree should not be attributed to a posiwith a normal baseline nutritional state, support should tive-pressure ventilation response and is more likely be initiated within 7 days. Parenteral nutrition is an alternative to enteral nutrition in patients with severe Removal of mechanical ventilator support requires that gastrointestinal pathology. Upper airway function must be intact for a patient to remain extubated but is difficult to assess in the intubated patient. Pulmonary complications include barofunction are assessed by observation of respiratory rate, trauma, nosocomial pneumonia, oxygen toxicity, tracheal tidal volume, inspiratory pressure, and vital capacity. Alveolar ventilation is deemed adequate when significant pneumothorax requires tube thoracostomy. Because this condition are best for patients intubated for extended periods likely is associated with high mortality rate, early initiation of to require gradual respiratory muscle reconditioning. Rates of >25 breaths/min on sures in patients with the acute respiratory distress syndrome. Irrespective of cause, the hypoperfusionControl of any inciting pathologic process. Multiple classification schemes mise perfusion through functional and structural have been developed in an attempt to synthesize the changes within the microvasculature. Strict vicious circle in which impaired perfusion is responsible adherence to a classification scheme may be difficult from for cellular injury, which causes maldistribution of blood a clinical standpoint because of the frequent combination fiow, further compromising cellular perfusion; the latter of two or more causes of shock in any individual patient, causes multiple organ failure and, if the process is not but the classification shown in Table 28-1 provides a interrupted, leads to death. The clinical manifestations of useful reference point from which to discuss and further shock are the result, in part, of autonomic neuroendelineate the underlying processes. However, when mean arterial pressure decreases to dioxide, nutrients, and products of metabolism through fi60 mmHg, fiow to these organs decreases, and their functhe interstitium; and the exchange of these products tion deteriorates. Impairment of the microcirculaArteriolar vascular smooth muscle has both fiand tion, which is central to the pathophysiologic responses fi-adrenergic receptors. The fi1 receptors mediate vasoconin the late stages of all forms of shock, results in the striction, and the fi2 receptors mediate vasodilation. Other constrictor substances that are increased in through alterations in hydrostatic pressure and osmolarity. Both norepinephrine capillary hydrostatic pressure and the number of capillary and epinephrine are released by the adrenal medulla, and beds perfused, thereby limiting the capillary surface area across which filtration occurs. Metabolic changes (including hyperHypovolemic Septic glycemia and elevations in the products of glycolysis, Traumatic Hyperdynamic Cardiogenic Hypodynamic lipolysis, and proteolysis) increase extracellular osmolarity, Intrinsic Neurogenic leading to an osmotic gradient between cells and interstiCompressive Hypoadrenal tium that increases interstitial and intravascular volume at the expense of intracellular volume. Low levels of cortisol in response to stimulation are linked to a Interstitial transport of nutrients is impaired in shock, decrease in survival. The importance of the cortisol leading to a decline of intracellular high-energy phosresponse to stress is illustrated by the profound circulaphate stores.
Buy brahmi 60caps low price
A anisms but there is no selection on pathogens to evade disease greater viral diversity may increase the chances that at tolerance mechanisms, resistance traits will be more polymorleast a few viral variants are able to successfully establish an phic in a population than tolerance traits (Roy and Kirchner, infection in the novel host. We note that immune tolerance as defined by diminished that have either chronically high virus levels or repeated tranimmune responses to a given antigen is only one component of sient high pathogen burdens in their natural hosts may be disease tolerance. The concept of disease tolerance was first overrepresented among emerging viral pathogens in humans examined in the context of selective pressures exerted by par(Figure 1). Characterthat result in superior pathogen replication control may also izing disease tolerance mechanisms is of particular importance be the responses that lead to increased collateral damage. An immunologic understandattenuated immune responses may result in waning immunoing of reservoir host species biology will include the study of all logic memory. Whether a tradeoff between resistance and ship between resistance and tolerance, although it may be the tolerance is a generalized phenomenon remains to be investicase that such a link would only become apparent over a Cell 160, January 15, 2015 fi2015 Elsevier Inc. Reservoir Host Infection and Disease Tolerance A feature of zoonotic infections in an individual naturalhostmaybethetoleranceofhighpathogen burdens in the absence of substantial deviation from health. Phase plots (adapted from Schneider and Ayres [2008]) illustrating possible infection trajectories following infection to highlight differences between novel and reservoir hosts in the extent of viral replication, viral kinetics, and associated disease burden. Transmission of zoonotic viruses may be more likely in cases in which there are persistently high viral loads or repeated acute infections ofreservoirhosts. Withinapopulationof the reservoir host, repeated infections with a pathogen may occur as a result of waning immunological memory within individuals, circulation of diverse strains to which there is minimal crossreactive immunity, or the introduction of new susceptible individuals (juveniles). To what extent and in which instances features of the immune responseinreservoirhostscontribute topathogen maintenance in a population is an important open question. In high levels of viremia and little evidence of effective immune the absence of symptoms in disease-tolerant reservoir hosts, control (Pandrea and Apetrei, 2010; Silvestri et al. Whereas Nipah and Hendra virus is primareven in the presence of high antibody titers (Easterbrook and ily respiratory in horses and pigs, transmitting oro-nasally (GeisKlein, 2008; Schountz and Prescott, 2014). For most zoonotic viruses, the transmission mode bestrains are associated with distinct host species, suggestive tween reservoir hosts remains unknown. Studying immune responses of reservoir hosts to their viruses In contrast, infections of wild waterfowl (Anas platyrhynchos) provides a unique opportunity to define molecular mechanisms with infiuenza A virus were shown to be transient (Jourdain underlying disease tolerance and to identify therapeutic targets et al. Given the high prevalence of seropositivity and to prevent the dysregulated immunopathology that often characthe presence of an enormous diversity of infiuenza A strains preterizes infections of novel hosts. Innate impartially protected from infection with co-circulating viral strains, munity and mechanisms of recognizing viral invasion of cells are but this requires further investigation. In pteropid fruit bat spean important first line of host defense, and signals downstream cies, infections with Hendra and Nipah viruses are likely also of innate immune receptors play a key role in the magnitude of transient, but few experimental infection studies have been the immune response initiated (Iwasaki, 2012). Viruses can done so far and the infection incidence is currently unknown trigger endosomal, cell surface, or cytosolic innate immune (Halpin et al. These viruses have receptors in a nucleic-acid-dependent manner (by their wholebeen detected at a prevalence of around 1% or less, although genome, replication products or intermediates) or in a nucleicseroprevalence can be as high as 60% (Breed et al. Given the seasonal and synchronous breeding general changes associated with cellular stress (Iwasaki, of these bats, it is difficult to distinguish whether there are sea2012).
Syndromes
- Lack of energy
- How much stress you are under
- Hansen disease (leprosy)
- No urine output or decreased urine output
- Are alcoholic
- Cervical discharge
- Severe pain and swelling
- Bleeding
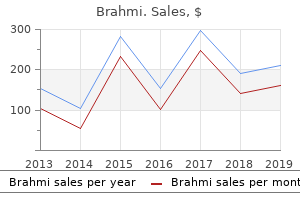
Purchase discount brahmi
Monkeypox virus is a species of the genus Orthopoxvirus, with biological properties and a genome map distinct from variola virus. There is no evidence that monkeypox will become a public health threat outside of enzootic areas. As the nodule grows, lymphatics draining the area become firm and cord-like and form a series of nodules, which in turn may soften and ulcerate. An epidemic among gold miners in South Africa involved some 3000 people; fungus was growing on mine timbers. Outbreaks have occurred among children playing in and adults working with baled hay. Preventive measures: Treat lumber with fungicides in industries where disease occurs. Wear gloves and long sleeves when working with sphagnum moss, and use personal protection when handling sick cats. In the South African epidemic, mine timbers were sprayed with a mixture of zinc sulfate and triolith in order to control the epidemic. A pus-containing lesion (or lesions) is the primary clinical finding, abscess formation is the typical pathological manifestation; production of toxins may also lead to staphylococcal diseases, as in toxic shock syndrome. However, coagulase-negative strains are increasingly important, especially in bloodstream infections among patients with intravascular catheters or prosthetic materials, in female urinary tract infections and in nosocomial infections. Staphylococcal disease has different clinical and epidemiological patterns in the general community, in newborns, in menstruating women and among hospitalized patients; each will be presented separately. Staphylococcal food poisoning, an intoxication and not an infection, is also discussed separately (see Foodborne intoxications, section I, Staphylococcal). Usually, lesions are uncomplicated, but seeding of the bloodstream may lead to pneumonia, lung abscess, osteomyelitis, sepsis, endocarditis, arthritis or meningitis.
Buy generic brahmi 60 caps line. Doctor's Notes - What is MS? Who gets MS? What are the symptoms? - April 2017.