"Buy genuine azithromycin, virus 1999 full movie".
By: P. Myxir, M.A., M.D., M.P.H.
Clinical Director, Medical College of Georgia at Augusta University
Generic azithromycin 100 mg
If such a model expresses a phenotype similar to the human disease, it is likely that the particular gene variation does cause disease. The Meesmann corneal dystrophy-like phenotype of the keratin 12 knock-out mouse[14] is an excellent example of this type of evidence for disease causation. The term dystrophy? has been used in the ophthalmic literature to refer to various types of disorders. Some dystrophies appear more sporadic than inherited, such as epithelial basement membrane dystrophy. Other disorders that are historically considered dystrophies are often asymmetric or unilateral, such as posterior polymorphous dystrophy. Edges of overlapping epithelial layers can be seen as curvilinear lines (fingerprints). A subepithelial haze may be present and, in the Smolandiensis variant, may be prominent enough to require corneal transplantation. Only one family has been reported and the gene that causes corneal disease in this family has not been identified. Patients are generally asymptomatic unless the opacities extend to the central cornea. In the second and third decades of life the visual acuity is reduced as the corneal haze and irregular surface progresses. However, the opacities can be differentiated by their honeycombed pattern and a clear zone near the corneoscleral limbus. Subepithelial fibrous tissue accumulates in wavelike patterns and is seen as the characteristic curly? fibers on transmission electron microscopy. The distinction between Reis-Bucklers and Thiel-Behnke corneal dystrophies has been a focus of controversy. In several early reports, descriptions of Reis-Bucklers dystrophy were based on patients that actually had Thiel-Behnke dystrophy. The inheritance appeared to be autosomal dominant, but no information about a chromosomal locus or causative gene is known. Linkage studies demonstrated that lattice, granular, and Avellino corneal dystrophies all mapped to the same chromosomal location at 5q31,[36] suggesting that they were caused by different variations in the same gene. It was more than a little surprising to many clinicians to learn that the breadcrumb-like corneal deposits of granular dystrophy and the branching lines of lattice dystrophy were caused by mutations in the same gene. Specifically, alterations involving the arginine amino acids at positions 124 and 555 of the encoded protein were found to be responsible for these diseases.
Buy genuine azithromycin
Streaming of Z-disc material, Z-disc duplication, and zig-zag irregularities are the most common lesions. Discrete osmiophilic cytoplasmic bodies, thought to be related to Z-discs, noted in a wide range of diseased myofbers. Mitochondria Swelling, with deposition of osmiophilic material or formation of myelin fgures, common and non-specifc. Re-orientation of intermyofbrillar mitochondria (in relation to myofber) occurs in a range of diseases. Structural abnormalities common (some associated with biochemical defciencies) and pres ent in a wide range of diseases, including the mitochondrial myopathies? and mitochondrial encephalomyopathies. Electron-dense granules and crystalline inclusions present in a wide range of diseases. Coalescence of T-system tubules to give a honeycomb pattern may be present in a wide range of diseases. Sarcoplasmic Dilation of cisternae prominent in periodic paralyses and some other diseases. Cylindrical structures in a spiral pattern, and with a core of glycogen, observed in a variety of diseases. Inclusions and Filamentous bodies, concentric laminated bodies, zebra-striped bodies, fngerprint bodies, deposits reducing bodies, spheroidal bodies, and paracrystalline arrays present in the sarcoplasm in a range of diseases. Glycogen moderately increased in a range of diseases; massively increased in various glycogenoses. Autophagic vacuoles and lipopigments present in degenerative diseases and in almost any myopathic state. In affected vessels electron-dense Cornea material (arrowhead) is seen in close proximity to the peri cytes or perivascular smooth muscle cells. Within the ensure that enough tissue is screened, it is recom ciliary shaft there is a core of microtubules (the mended that a minimum of three blocks and 50 ves axoneme) composed of nine outer pairs of micro sels are observed. Primary defects are caused by a heteroge lar electron-dense granular material which is often neous group of genetic abnormalities which result in contact with the vascular pericytes and smooth in immotile cilia syndrome, primary ciliary dys muscle cells, and sited in a small indentation (Fig. However, it should also be noted that not all genetic cilia defects result in abnormal ciliary morphology (Santamaria et al. Intracellular fbrillary crystalloids (arrowheads) in the cytoplasm of a corneal keratinocyte. Schematic cross-section through the middle of a normal ciliary shaft to show the structure of the axoneme. The axoneme is formed from an outer ring of nine microtubule pairs with one central pair (the 9 + 2 confguration).
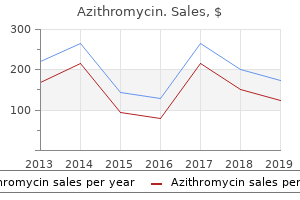
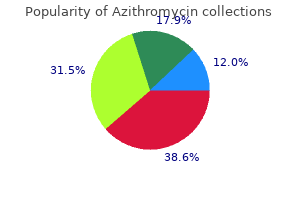
Order 250 mg azithromycin free shipping
Remediation also includes household filters, phytoremediation and solar-light assisted arsenic removal. This reaction process is very fast for permanganate, chlorine and ozone in comparison to hydrogen peroxide and chloroamine. Potassium permanganate effectively oxidizes As, and it is inexpensive and suitable for developing countries. Hydrogen peroxide is an effective oxidant if the untreated water contains dissolved iron, which occurs in conjunction with arsenic contamination, allowing the occurrence of Fenton reactions. Disadvantages: An adequate selection of oxidants in relation with aquatic chemistry and water composition is a pertinent step to achieve a high removal efficiency of aqueous arsenic by oxidation. Due to several drawbacks, oxidation alone is not an effective method for removal of arsenic. Although the coagulation process is a simple and economically sound one, it produces a wet bulky sludge. Principle: Chemicals such as aluminum sulfate, ferric chloride and ferrous V sulfate, iron salts are used to remove arsenic (As), which adsorbs onto 138. Iron chloride generates relatively large flocs, while smaller ones are formed with ferrous sulfate. Advantages: It is a simple, most common, effective and low cost method V acting over wide range of pH. Further environmental pollution occurs due to improper disposal of contaminated sludge. Activated alumina has long been the most often used adsorbent for arsenic removal. The problems including the need for pH adjustment, the relatively low adsorption capacity, and aluminum dissolution have prevented activated alumina from wider applications. Cerium: An iron based inorganic adsorbent, developed by doping cerium ions V into iron ions, is used for As removal. In terms of adsorption pH range and adsorption capacity, the new adsorbent demonstrated a much better performance than activated alumina (Zhang et al. The three or four-pitcher filter is based on an indigenous method of filtration, which has been used in Bangladesh for ages to remove excess iron and calcium from drinking water. The household level filtration device was designed to remove both arsenic and pathogenic bacteria. The Safi filter candle is prepared from a chemical mixture of laterite soil, ferric oxide, manganese di-oxide, aluminum hydroxide and meso-porous silica. These materials adsorb arsenic as the water passes through the candle and thus the contamination is removed. The top pitcher is partially filled with sand and charcoal, and a small hole is made in the bottom.
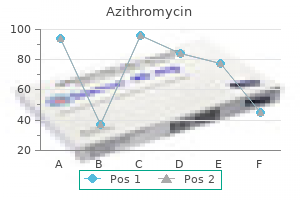
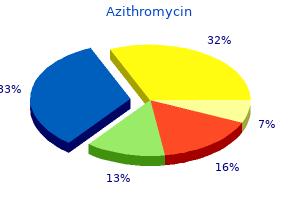
Generic azithromycin 500 mg with mastercard
Associated reversible neurologic defcits (rare): Paresthesia, visual-feld cuts, aphasia, hemiplegia, ophthalmoplegia, vertigo, ataxia, confusion. These children typically receive neuroimaging due to the complicated nature of their migraines 4. Treatment6: Includes reassurance and education regarding lifestyle modifcation (sleep, exercise, stress reduction, fuids, not missing meals). The acute and chronic pharmacologic treatment of migraine headaches in the pediatric population is well studied; however, these recommendations have not yet been incorporated into national guidelines for children a. Chapter 20 Neurology 511 (3) For >12 years of age: Objective data support nasal sumatriptan. Chronic treatment (if >3 per month and if migraines interfere with daily functioning or school): (1) Avoid triggers and stress, improve general health with balanced diet restrictive of certain migraine-causing foods, suggest headache journal to help identify potential triggers. Offer counseling when appropriate; also consider biofeedback, acupuncture, yoga, massage therapy if parents are interested (3) Consider medications. See Table 20-4 for summary of preventive therapies, doses, and adverse effects (4) the natural history of chronic headache includes spontaneous improvement. Differential Diagnosis of Recurrent Events that Mimic Epilepsy in Childhood (Table 20-5) B. Seizure: Paroxysmal synchronized discharge of cortical neurons, resulting in alteration of function (motor, sensory, cognitive) 2. Diffuse brain dysfunction: Fever, metabolic compromise, toxin or drugs, hypertension, idiopathic epilepsy b. Focal brain dysfunction: Stroke, neoplasm, focal cortical dysgenesis, trauma, focal idiopathic epilepsy 3. Short duration (no more than 10 minutes) and rapid recovery (if not meningitis should be high on the differential) 4. Paroxysmal vertigo Patient frightened and crying; no loss of awareness; staggers (toddler) and falls, vomiting, dysarthria. Breath-holding spells Loss of consciousness and generalized convulsions, always (18 mo?3 yr) provoked by an event that makes child cry. Syncope Loss of consciousness with onset of dizziness and clouded or tunnel vision; slow collapse to foor; triggered by postural change, heat, emotion, etc. Cough syncope Prolonged cough spasm during sleep in asthmatic, leading to loss of consciousness, often with urinary incontinence. Paroxysmal May be precipitated by sudden movement or startle; not dyskinesias accompanied by change in alertness. Night terrors (4?6 yr) Brief nocturnal episodes of terror without typical convulsive movements. Tics/habit spasms Involuntary, nonrhythmic, repetitive movements not associated with impaired consciousness; suppressible. Starting as simple partial seizures (a) Without automatisms (b) With automatisms (such as lip smacking and drooling, dazed eyes look) 2. With impairment of consciousness at onset (a) Without automatisms (b) With automatisms C.
Generic azithromycin 100 mg. The Lab Report Episode 9: Analysis of Wear Metals in New and Used Oil.