"Purchase online zyban, anxiety in teens".
By: D. Ernesto, M.B.A., M.D.
Medical Instructor, Donald and Barbara School of Medicine at Hofstra/Northwell
Order online zyban
Systematic review of tests to identify the disc, sij or facet joint as the source of low back pain. Lumbar stiffness disability index: Pilot testing of consistency, reliability, and validity. Evidence based orthopaedic manual therapy for patients with nonspecific low back pain: An integrative approach. Intertester agreement and validity of identifying lumbar pain provocative movement patterns using active and passive accessory movement tests. Use of kinematic algorithms to distinguish people with chronic non-specific low back pain from asymptomatic subjects: A validation study. Multidisciplinary biopsychosocial rehabilitation for chronic low back pain: Cochrane systematic review and meta analysis. Building cooperation in peer coaching relationships: Understanding the relationships between reward structure, learner preparedness, coaching skill and learner engagement. Comparing lumbo-pelvic kinematics in people with and without back pain: A systematic review and meta-analysis. The clinical reasoning processes of extended scope physiotherapists assessing patients with low back pain. Multivariable analysis of the relationship between pain referral patterns and the source of chronic low back pain. Controlling for out-of-plane lumbar moments during unidirectional trunk efforts: Learning and reliability issues related to trunk muscle activation estimates. Journal of electromyography and kinesiology: official journal of the International Society of Electrophysiological Kinesiology, 24, 531-41. Manual correction of an acute lumbar lateral shift: Maintenance of correction and rehabilitation: A case report with video. Reproducibility of lumbar spine range of motion measurements using the back range of motion device. A comparison of two motion analysis devices used in the measurement of lumbar spinal mobility. Combined movement theory: Rational mobilisation and manipulation of the vertebral column, Churchill Livingstone Elsevier.
Syndromes
- Pressure flow studies to measure the pressure in the bladder as you urinate
- Skin lesion
- Luteinizing hormone (LH) levels
- Breastfeeding should be avoided to prevent passing on HIV to infants through breast milk.
- Coughing, chest pains, or breathing problems if there are swollen lymph nodes in the chest
- · Use an over-the-counter pain medicine, such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen. (Talk to your doctor first if you have a history of ulcer or liver problems.)
- LP -- low platelet count
- Repeated urine cultures
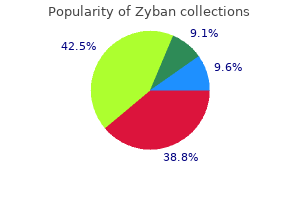
Purchase online zyban
Family stress and adjustment as perceived by parents of children with autism or Down syndrome: Implications for intervention. Meta-analysis of comparative studies of depression in mothers of children with and without developmental disabilities. Parent and teacher agreement in the assessment of pervasive developmental disorders. The relationship between behaviours exhibited by children with autism and maternal stress. Strossmayer in Osijek, Faculty of Philosophy, Department of Psychology Department of Public Health, Zagreb County Croatia 1. Introduction Autism is defined as an organic developmental brain disorder that is manifested in difficulties in social interactions and communication, as well as unusual behaviors (Volkmar& Pauls, 2003; Gillham et al. Fombonne, performed a meta-analysis of 32 epidemiological studies of autism spectrum disorders conducted between 1966 and 1991. Data was collected on the prevalence of autism spectrum disorders in 13 different countries on a sample of nearly five million inhabitants. Another study found that 60 people of 10, 000 live births have autism spectrum disorders (Fombonne, 2005). In the Global report data for Croatia are not included, but they are available from the Croatian Disabilities Registry. A series of studies has been published about subjective health and health-related quality of life of family caregivers. Previous studies on family caregivers of people with chronic health problems reviled higher level of burden, stress, and depression (Canam & Acorn, 1999). Although it has been argued that all chronic illnesses and disabilities of children can negatively affect health-related quality of life of the parents; each disease present unique challenges (Epstein et al. Caregivers also reported somewhat lower marital happiness, disturb family cohesion, and family adaptability (Higgins et al. Poor caregiver health may contribute to recurrent hospitalizations (Kelly& Hewson, 2000) and out-of-home placements for children with chronic conditions and disabilities (Bromley& Blacher, 1991; Llewellyn et al. The same institution administers rehabilitation and therapeutic measures for 333 persons. The inpatient unit accommodates 89 patients, 37 of whom never come into contact with their parents. This is one of the aspects of community efforts to provide social support which are one of the important factors for these families (Whitaker, 2002; Brown et al. The control group was 172 parents of non-disabled children, median age 42 yrs (24-82 yrs), of which 101 were mothers (58. A majority of respondents in both groups were married, though a higher number of single parent families existed in the group of parents of children with autism spectrum disorders (11.
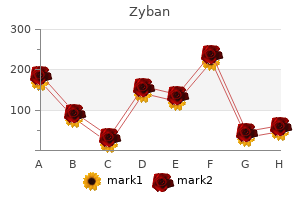
Order zyban 150 mg without prescription
In many an giosperms, for example, mitochondrial and chloroplast genes from different indi viduals do not recombine in crosses where they are inherited uniparentally. If cells from two parents are fused, recombinant genotypes are readily detected for mitochondrial genes, but recombinant chloroplast genomes are rare and can only be detected after stringent selection. When recombinants for two different antibiotic resistance genes are selected, other markers on the selected genomes show extensive recombination (59). This shows that plant chloroplasts do have the enzymatic machinery required for recombination but the chloroplasts rarely fuse. Although plant organelle genomes from different lineages rarely have an op portunity to recombine, intramolecular and intermolecular recombination within a lineage can still occur. Repeated rounds of random pairing and gene conversion could cause in tracellular random drift (12), but so far it has not been possible to determine how important this is, relative to stochastic replication. One might imagine that when organelle genes are inherited biparentally, they would still show less re combination on average than nuclear genes because they are all on one chromo some. But this is not necessarily so: In Saccharomyces cerevisiae, the genomes in a zygote and its early buds undergo repeated rounds of pairing and recom bination, resulting in recombination frequencies of about 1% per 100 bp (97). In principle, this approach could detect pa ternal inheritance and recombination because it analyzes the pooled results of very large numbers of matings taking place over long time periods. However, their data sets contained signi cant errors, and when these were corrected the argument that homoplasy is due to recombination was weak ened (55). Al though the logic of this test is correct, the results were challenged on method ological grounds, and some additional data sets were found not to show a sig ni cant negative correlation between distance and disequilibrium (see discussion at. The subject was nicely reviewed by Eyre-Walker (28), who noted that only 9 of 14 human data sets show the negative correlation and none was signi cant. On the other hand, a chimpanzee data set did show a signi cant negative correlation, and the majority of the data seem to point in that direction. They review biochemical evidence that mammalian mitochondria contain at least some of the enzymes required for intramolecular recombination. However, when they cultured cells that were heteroplasmic for the wild-type and deletion genomes, they found none of the dimers that would result from intermolecular recombination. They suggest that this may be because the two genomes were initially in separate cells that were fused to make heteroplasmic cybrids; consequently, they may have remained physically isolated from each other, in different organelles or different regions of an organelle. On the other hand, they argue that the dimeric mutants were almost certainly originally formed by a combination of intramolecular and intermolecular recombination between two molecules in the same cell. These authors (89) also point out that triplicated mitochondrial genomes found by Holt et al. Finally, the time is ripe to apply a combination of genetic, molecular, and cytologi cal methods to determining the relative importance of these mechanisms in speci c cases.
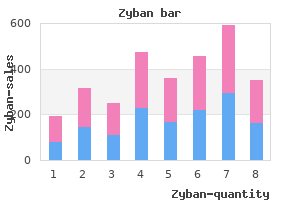
Buy 150 mg zyban with visa
These include rupture of a deep ce (the lower eye on the side of the lesion); gaze rebral endartery, amyloid angiopathy, mycotic preference, which may either be toward or aneurysm, arteriovenous malformation, or hem away (wrong-way eyes) from the side of the orrhage into a tumor, and each requires a dif lesion; loss of vertical gaze; and miotic pupils. Sensory and motor differentiate clinically between acute cerebral disturbances depend on the site and size of the vascular lesions potentially causing stupor or 101 lesion. The blood vessels that are most likely primary or result from extension of an intra to hemorrhage are the same ones that cause cerebral hemorrhage. Pri perforating arteries, which give rise to thalamic mary intraventricular hemorrhages can result hemorrhages; the midline perforating arteries from vascular anomalies within the ventricle, of the pons, which give rise to pontine hemor surgical procedures, or bleeding abnormali rhages; and the penetrating branches of the 104 ties. Clinical ndings include sudden onset cerebellar long circumferential arteries, which of headache and vomiting sometimes followed cause cerebellar hemorrhages. If the hemorrhage nds with the rst two, which cause supratentorial its way into the subarachnoid space, nuchal masses, in this section, and the latter two in the rigidity occurs. Hemorrhage into are characteristic of the part of the brain that the ventricle from a primary intracerebral hem is injured. Obtundation from the start or within hours, progressing to stupor in 12 to 24 hours, coma usually in 36 to 96 hours. Conjugate gaze paresis to side of motor weakness; contralateral oculovestibulars can be sup pressed for 12 hours or so. Contralateral hemiplegia, usually with extensor plantar response and paratonia ipsilateral to lesion. Sudden-onset headache, followed by more or less rap idly evolving aphasia, hemiparesis to hemiplegia, conjugate ocular deviation away from hemiparesis. Clinical picture similar to frontoparietal hemorrhage but seizures rare, vomiting frequent, eyes characteristically deviated down and laterally to either side. Sudden onset of coma or speechlessness, pinpoint pupils, ophthal moplegia with absent or impaired oculovestibular responses, quadriplegia, irreg ular breathing, hyperthermia. Acute and rapid onset and worsening within hours of occipital headache, nausea and vomiting, dizziness or vertigo, unstead iness, dysarthria, and drowsiness. Small and reactive pupils, nystagmus or hori zontal gaze paralysis toward the side of the lesion. Midline and ipsilateral ataxia, (continued) 138 Speci c Causes of Structural Coma 139 ipsilateral peripheral facial palsy, and contralateral extensor plantar response. Vertigo, ataxia, nausea, dull headache, nystagmus, dysarthria, ipsilateral dysmetria; 24 to 96 hours later: drowsiness, miosis, ipsilateral gaze paresis and facial paresis, worsening ataxia, extensor plantar responses. Acute subarachnoid hemorrhage Awake at onset, sometimes hypertensive, sudden headache, often followed within minutes by unconsciousness.
Order online zyban. The 6 Signs of High Functioning Depression | Kati Morton.