"Discount 500 mg robaxin amex, spasms meaning in hindi".
By: E. Barrack, M.A., M.D.
Co-Director, Rutgers New Jersey Medical School
Robaxin 500mg low cost
This includes meningitis, encephalitis or acute flaccid paralysis or poliomyelitis-like syndrome. The disease can also progress severely, particularly in older people and people with weakened immune systems, sometimes resulting in permanent cognitive limitations or death [133]. Since virus-specific IgM antibodies can persist in serum or plasma for up to a year, a quadrupling or more of the antibody titers in samples taken during the course of the acute or convalescence phase is required for conclusive clarification. The clinical relevance of serological methods for detecting antibodies is limited by the wide antigen cross reactivity between flaviviruses. This test is laborious and is usually only offered by reference and specialist laboratories. However, viremia is short (with low virus concentrations) and limited to the early phase of the disease. There are two lines, the African and the Asian, which have around a 4% variability at the amino acid level. The virus was first isolated in 1947 in the Zika forest in Uganda in blood taken from a rhesus monkey. Before then only very sporadic human cases had been reported since the discovery of the virus. Starting in 2013, the Zika virus led to outbreaks on various other Pacific islands, such as the Cook Islands, Marshall Islands, French Polynesia, Easter Island etc. The virus strain was the Asian line which suggests that it originated in the Pacific islands. Since 2015 the Zika virus has spread rapidly throughout South America, into Central America and the Caribbean and ultimately to Mexico. By April 2016 it had been identified in 64 countries and had led to several million infected individuals (go to Of special importance is the prenatal transmission of the virus from pregnant women to their unborn children. In Germany, people returning from outbreak regions must defer donating blood for four weeks. If symptoms do appear, the clinical picture (Zika fever) is similar to dengue fever. Symptoms are milder on the whole and, in addition to fever, maculopapular exanthem, headaches and muscle ache, they are often associated more with conjunctivitis and arthralgia. When pregnant women are infected, the Zika virus can be transmitted to the newborn child and cause a fetal infection that can be accompanied by deformities. The risk of fetal deformation appears to be particularly high when the maternal infection occurs within the first trimenon. Based on what happened during the outbreak in French Polynesia, the risk of microencephaly is estimated to be 1% if the mother had experienced a Zika virus infection in the first trimester of pregnancy [51]. If there has been a dengue virus infection in the past, an acute Zika virus infection can trigger the 181 production of IgM antibodies specific to the dengue virus.
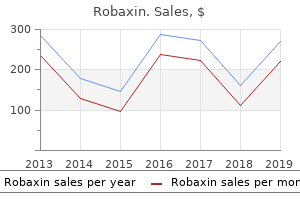
Order robaxin uk
Co-infection with different microsporidia or other enteric pathogens can occur and microsporidiosis may be linked to travel or residence in the tropics/developing countries (Weiss 2001). Disease incidence Prevalence of microsporidia in studies of patients with chronic diarrhoea range from 7% to 50% with the differences in range attributable to factors such as risk factors, diagnostic capability and geographic variation (Slifko et al. Microsporidial spores are stable in the environment and remain infective for days to weeks outside their hosts. The biological features of microsporidia that favour waterborne transmission are outlined in Table 5. Risk factors identified included swimming in rivers, ponds and lakes and drinking unfiltered tap water. Arcay (2000) has identified microsporidia in an array of river and lakewaters in Venezuela. The study concluded that swimming pools are rarely contaminated with microsporidia and the risk of contamination through swimming pools is limited. In the summer of 1995, 200 people (82% of which were immunocompromised) suffered a waterborne outbreak of microsporidiosis with no evidence of faecal contamination. These patients lived preferentially in an area corresponding to one of the three water distribution systems of Lyon, France suggesting contaminated water. Unfortunately this was a retrospective study and it was therefore not possible to sample the water distribution system for the presence of microsporidia. Factors that may have contributed to contamination include pumping of surface water directly from a recreational area that is mainly frequented by swimmers in summer. Treatment of this water was by flocculation, ozoflotation and filtration instead of by chlorination as at the other two treatment facilities. Diatomeaceous earth filters used in swimming pools will not filter out microsporidia spores so treatments such as chlorination or ozone are the only possible prevention methods (Hutin et al. Limited work has suggested microsporidia are susceptible to achievable chlorine concentration versus time values (Mota et al.
Discount 500 mg robaxin amex
For a health professional in If blood tests reveal the presence of an acute kidney injury, or if the lactate is found to be higher than 2 hospital, this will be to ensure delivery of the Sepsis 6. Discharge from hospital, possibly with oral antibiotics, may be appropriate with safety netting and consideration given to a scheduled review. Health professionals outside hospital should consider whether the patient can safely be cared for in the community or requires hospital assessment (with appropriate documentation of the decision and If neither a Red Flag nor an Amber Flag are present, this indicates a low risk of adverse outcome from safety netting if the patient is to be managed in the community). Other conditions should be considered, and recommends that a single Amber Flag should prompt consideration of the need for blood tests (to include standard protocols followed. When a person has pneumonia, the lungs become flled with microorgan isms, fuid, and infammatory cells which make the work of breathing difcult and prevent the lungs from working properly. Diagnosis of pneumonia is based on the signs and symptoms of an acute lower respiratory tract infection. In the later stages of this condition impending respiratory failure might be recognised through the development of cyanosis, severe fatigue or even a reduced conscious level due to exhaustion or hypercapnia. If you suspect your patient may have an atypical pneumonia it is otherwise healthy young men. A urinary tract infection can result in several clinical syndromes, including acute and chronic accounting for between 15 and 20% of cases. Intra-abdominal infections commonly arise from the biliary pyelonephritis (infection of the kidney and renal pelvis), cystitis (infection of the bladder), urethritis tract. Peritoneal contamination may result from mishandling of bowel contents during surgery, or from Symptoms reported can include dysuria, frequency, ofensive-smelling or discoloured urine, loin pain and trauma or a spontaneous perforation (for example, appendicitis, perforated ulcer or diverticulitis). Symptoms tend to be localised initially (such as in Common organisms causing urinary tract sepsis are gram-negative bacteria such as E. Whatever the cause, the presence of a purpuric rash in the Diagnosis context of suspected infection is a medical emergency and demands the highest level of skill and experience available.
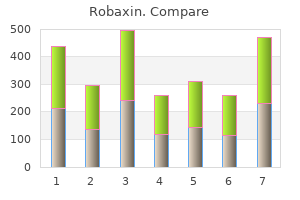
Cheap robaxin 500mg with mastercard
Navigational Note: Retinal tear No retinal detachment and No retinal detachment and treatment not indicated treatment indicated Definition:A disorder characterized by a small laceration of the retina, this occurs when the vitreous separates from the retina. Navigational Note: Vision decreased Moderate decrease in visual Marked decrease in visual Best corrected visual acuity of acuity (best corrected visual acuity (best corrected visual 20/200 or worse in the acuity 20/40 and better or 3 acuity worse than 20/40 or affected eye lines or less decreased vision more than 3 lines of from known baseline) decreased vision from known baseline, up to 20/200) Definition:A disorder characterized by a decrease in visual acuity. Navigational Note: Ascites Asymptomatic; clinical or Symptomatic; medical Severe symptoms; invasive Life-threatening Death diagnostic observations only; intervention indicated intervention indicated consequences; urgent intervention not indicated operative intervention indicated Definition:A disorder characterized by accumulation of serous or hemorrhagic fluid in the peritoneal cavity. Navigational Note: Chylous ascites Asymptomatic; clinical or Symptomatic; medical Severe symptoms; elective Life-threatening Death diagnostic observations only; intervention indicated. Navigational Note: Colitis Asymptomatic; clinical or Abdominal pain; mucus or Severe abdominal pain; Life-threatening Death diagnostic observations only; blood in stool peritoneal signs consequences; urgent intervention not indicated intervention indicated Definition:A disorder characterized by inflammation of the colon. Navigational Note: Dental caries One or more dental caries, Dental caries involving the Dental caries resulting in not involving the root root pulpitis or periapical abscess or resulting in tooth loss Definition:A disorder characterized by the decay of a tooth, in which it becomes softened, discolored and/or porous. Navigational Note: Duodenal fistula Asymptomatic Symptomatic, invasive Invasive intervention Life-threatening Death intervention not indicated indicated consequences; urgent intervention indicated Definition:A disorder characterized by an abnormal communication between the duodenum and another organ or anatomic site. Navigational Note: Duodenal hemorrhage Mild symptoms; intervention Moderate symptoms; Transfusion indicated; Life-threatening Death not indicated intervention indicated invasive intervention consequences; urgent indicated; hospitalization intervention indicated Definition:A disorder characterized by bleeding from the duodenum. Navigational Note: Esophageal fistula Asymptomatic Symptomatic, invasive Invasive intervention Life-threatening Death intervention not indicated indicated consequences; urgent intervention indicated Definition:A disorder characterized by an abnormal communication between the esophagus and another organ or anatomic site. Navigational Note: Esophageal perforation Invasive intervention not Invasive intervention Life-threatening Death indicated indicated consequences; urgent operative intervention indicated Definition:A disorder characterized by a rupture in the wall of the esophagus. Navigational Note: Gingival pain Mild pain Moderate pain interfering Severe pain; inability to with oral intake aliment orally Definition:A disorder characterized by a sensation of marked discomfort in the gingival region. Navigational Note: Hemorrhoidal hemorrhage Mild symptoms; intervention Moderate symptoms; Transfusion indicated; Life-threatening Death not indicated intervention indicated invasive intervention consequences; urgent indicated; hospitalization intervention indicated Definition:A disorder characterized by bleeding from the hemorrhoids. Navigational Note: Ileal fistula Asymptomatic Symptomatic, invasive Invasive intervention Life-threatening Death intervention not indicated indicated consequences; urgent intervention indicated Definition:A disorder characterized by an abnormal communication between the ileum and another organ or anatomic site. Navigational Note: Intra-abdominal hemorrhage Moderate symptoms; Transfusion indicated; Life-threatening Death intervention indicated invasive intervention consequences; urgent indicated; hospitalization intervention indicated Definition:A disorder characterized by bleeding in the abdominal cavity. Navigational Note: Jejunal fistula Asymptomatic Symptomatic, invasive Invasive intervention Life-threatening Death intervention not indicated indicated consequences; urgent intervention indicated Definition:A disorder characterized by an abnormal communication between the jejunum and another organ or anatomic site. Navigational Note: Jejunal hemorrhage Mild symptoms; intervention Moderate symptoms; Transfusion indicated; Life-threatening Death not indicated intervention indicated invasive intervention consequences; urgent indicated; hospitalization intervention indicated Definition:A disorder characterized by bleeding from the jejunal wall. Navigational Note: Lower gastrointestinal Mild symptoms; intervention Moderate symptoms; Transfusion indicated; Life-threatening Death hemorrhage not indicated intervention indicated invasive intervention consequences; urgent indicated; hospitalization intervention indicated Definition:A disorder characterized by bleeding from the lower gastrointestinal tract (small intestine, large intestine, and anus). Navigational Note: Oral cavity fistula Asymptomatic Symptomatic, invasive Invasive intervention Life-threatening Death intervention not indicated indicated consequences; urgent intervention indicated Definition:A disorder characterized by an abnormal communication between the oral cavity and another organ or anatomic site. Navigational Note: Periodontal disease Gingival recession or Moderate gingival recession Spontaneous bleeding; severe gingivitis; limited bleeding on or gingivitis; multiple sites of bone loss with or without probing; mild local bone loss bleeding on probing; tooth loss; osteonecrosis of moderate bone loss maxilla or mandible Definition:A disorder in the gingival tissue around the teeth. Navigational Note: Rectal fissure Asymptomatic Symptomatic Invasive intervention indicated Definition:A disorder characterized by a tear in the lining of the rectum. Navigational Note: Rectal hemorrhage Mild symptoms; intervention Moderate symptoms; Transfusion indicated; Life-threatening Death not indicated intervention indicated invasive intervention consequences; urgent indicated; hospitalization intervention indicated Definition:A disorder characterized by bleeding from the rectal wall and discharged from the anus.
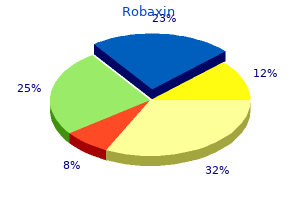
Quality 500 mg robaxin
Patients over 18 years of age were eligible if at least 6 tender and 6 swollen joints were present at baseline. From Week 16, non responding patients could be rescued to receive baricitinib 4 mg once daily. From Week 16, non-responding patients could be rescued to receive baricitinib 4 mg once daily. Instruct patients to tell their healthcare provider if they develop any signs or symptoms of an infection [see Warnings and Precautions (5. Instruct patients to inform their healthcare provider if they have ever had any type of cancer [see Warnings and Precautions (5. Ask your healthcare provider if you do not know if you have lived in an area where these infections are common. Keep a list of them to show your healthcare provider and pharmacist when you get a new medicine. Active ingredient: baricitinib Inactive ingredients: croscarmellose sodium, magnesium stearate, mannitol, microcrystalline cellulose, ferric oxide, lecithin (soya), polyethylene glycol, polyvinyl alcohol, talc, titanium dioxide. During the past year, she has had episodes of ear swelling and recurrent pain and swelling in the knees. For the past 6 months he has had numbness in the R foot pain and discoloration in some fingers of both hands. For the past 1 month, he has developed weakness of the L foot and ischemic lesions of the fingertips. He presents to the emergency room with severe abdominal pain/tenderness of 1 week duration. She was diagnosed with scleroderma 1 year ago when she presented with sclerodermatous skin changes on her fingers and face. Laboratory studies are normal except for an erythrocyte sedimentation rate of 30 mm/h.
Robaxin 500mg low cost. Freeze Trigger Hypnosis.