"Order 250mg diamox visa, symptoms 4 weeks 3 days pregnant".
By: P. Grubuz, M.S., Ph.D.
Professor, Northeast Ohio Medical University College of Medicine
Buy diamox 250 mg overnight delivery
Bupropion and its metabolites exhibit linear kinetics following chronic administration of 150 to 300 mg/day. The elimination of the major metabolites of bupropion may be affected by reduced renal or hepatic function because they are moderately polar compounds and are likely to undergo further metabolism or conjugation in the liver prior to urinary excretion. Geriatrics: the effects of age on the pharmacokinetics of bupropion and its metabolites have not been fully characterized, but an exploration of steady state bupropion concentrations from several depression efficacy studies involving patients dosed in a range of 300 to 750 mg/day, on a three times a day schedule, revealed no relationship between age (18 to 83 years) and plasma concentration of bupropion. A single-dose pharmacokinetic study demonstrated that the disposition of bupropion and its metabolites in elderly subjects was similar to that of younger subjects. Race: Page 27 of 45 the influence of race (Asian, Black and Caucasian) on the pharmacokinetics of bupropion (bupropion hydrochloride immediate release tablets) was evaluated based on dose normalized data pooled from five healthy volunteer studies. Hepatic Insufficiency the effect of hepatic impairment on the pharmacokinetics of bupropion was characterized in two single-dose studies, one in subjects with alcoholic liver disease and one in subjects with mild to severe liver cirrhosis. The first study involved 8 subjects with alcoholic liver disease, and 8 healthy matched controls. The mean half-life of the primary metabolite hydroxybupropion was significantly longer by approximately 40% in subjects with alcoholic liver disease than in healthy volunteers (32?14 hours versus 21?5 hours, respectively). For all other pharmacokinetic values, for both parent drug and metabolites, there were minimal differences between the two groups. The second study involved 17 subjects with hepatic impairment (n = 9 mild/Grade A child-Pugh rating; n = 8 severe/Grade C Child-Pugh rating) and 8 healthy matched controls. Mean Cmax and plasma half-life were increased by approximately 70% and 40% respectively. Mean Cmax was lower by approximately 30% to 70%, and mean plasma half life increased threefold. In the mild group, while mean values were not statistically increased from those of controls, the variability in the pharmacokinetic values was higher in the subjects with impairment; a sub-group of 1 to 3 subjects (dependent on pharmacokinetic parameter examined) showed individual values which were in the range of the severely impaired subjects. For the primary metabolites, the differences between groups in pharmacokinetic parameters were minimal. Effect of Smoking In a single dose study, there were no significant differences in the pharmacokinetics of bupropion or its major metabolites in smokers compared with non-smokers. Each 300 mg tablet contains the labeled amount of bupropion hydrochloride and the inactive ingredients: Denatured ethyl alcohol, ethylcellulose, glyceryl behenate, isopropyl alcohol, methylacrylic acid co-polymer dispersion, polyethylene glycol, polyvinyl alcohol, povidone, silicon dioxide, triethyl citrate, N-butyl alcohol, propylene glycol, shellac glaze, titanium dioxide, and iron oxide black. The majority of the subjects across the treatment groups were Female (61%), White (71%), with a mean age of 37 years. Treatment was initiated prior to the onset of symptoms in the autumn (September to November) and was discontinued following a 2 week taper that began the first week of spring (fourth week of March), resulting in treatment duration of approximately 4 to 6 months for the majority of patients. Patients who Page 32 of 45 were deemed by the investigator to be unlikely or unable to tolerate 300 mg once daily were allowed to remain? Recent data suggest that a significant contribution to the pharmacology of bupropion is made by one of its two major metabolites, hydroxybupropion.
Buy diamox 250 mg lowest price
Accordingly, a genetic diagnosis can be applied to individuals who have not yet developed any phenotypic expression. Therefore, these individuals have a genetic susceptibility to developing iron overload but may never do so, for reasons that are still to be deter6,10-12 mined. There is a short cytoplasmic tail expression only occurs in approximately 70% of and three extracellular alpha loops. Iron-loading anemias Thalassemia major the result is iron deposition primarily in macrophages, Sideroblastic and this disorder is called ferroportin disease?. Some individuAlcoholic liver disease als with African iron overload drink an iron-rich ferNonalcoholic fatty liver disease mented beverage, but iron overload can also occur in Following portocaval shunt 19 people who do not drink this beverage. Dysmetabolic iron overload syndrome Miscellaneous Causes of Secondary Iron Overload and MiscellaNeonatal iron overload neous Disorders. Individuals who absorb excessive Aceruloplasminemia amounts of iron as a result of an underlying defect Congenital atransferrinemia other than any of the previously mentioned inherited 20 disorders have secondary iron overload. Individuals who receive related to chronic liver disease, transfusional iron overblood transfusions and who have transfusional or parload, and miscellaneous causes. Hepcidin is a 25?amino acid pregnancy slows or prevents the development of this 22 peptide produced in the liver that down-regulates iron condition. Mutations in the TfR2 gene produce an congenital atransferrinemia and aceruloplasminemia. Kupffer resulting increases in iron absorption from the intescells become activated byproducts released from 25 tine and release of iron from macrophages. Summary of interactions between duodenal enterocytes, hepatocytes, and macrophages in iron homeostasis regulated by hepcidin. The reasons for the lack of phenotypic expresMore men than women have increased ferritin levels. It may involve interactions with Nonetheless, it is still important for clinicians to be gene products of other proteins involved in iron hoaware of the symptoms that patients may exhibit and meostasis (with or without mutation). Principal Clinical Features in Hereditary Hemochromatosis Study (Year) Features Milder et al. There are certain high-risk during pregnancy having a protective effect for groups that should be targeted for evaluation, such as women. Nonetheless, the proportion of C282Y generally recommended that all patients with abnormal homozygous women with de? We recommend that patients with abnormal iron studies should be evaluated as patients with hemochromatosis, even in the absence of symptoms.
Buy diamox 250 mg overnight delivery. ultrasound ka bagair jan skty hain maa k pet may larka hai ya larki.
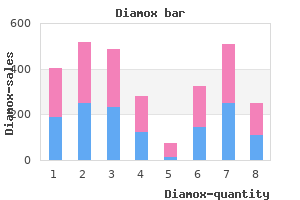
Order 250mg diamox visa
Certain weapons cause specifc burns: napalm and phosphorus bombs, magnesium fares and decoys. Nonetheless, this absolute prohibition cannot entirely exclude that a State or a nonState armed group resort to using them. A bomb surrounded by radioactive material the so-called dirty bomb is not a nuclear bomb. The explosion is caused by conventional means but, depending on the force of the explosion, radioactive material may be spread over a wide area. The bombing of nuclear medicine and other laboratory facilities, or nuclear power plants, may also release radioactive material into the atmosphere. While standard surgical techniques will sufce to treat simple wounds, the management of war wounds produced by high-energy weapons is based on an understanding of the mechanisms by which projectiles cause injury: wound ballistics. Only by understanding certain physical phenomena can the surgeon appreciate the diferent varieties of wounds seen in armed confict and the diference between these wounds and the trauma that is seen in everyday civilian practice. Although the study of ballistics may be interesting in its own right, the clinician does not always know what weapon inficted the injury; and never knows the energy available at point of impact. One can only estimate the transfer of energy in the tissues from the extent of tissue damage. The study of ballistics gives us an understanding of the basic mechanisms at work during wounding. The importance of this knowledge lies in the fact that projectile injuries should be neither undernor over-treated. The clinical assessment of the actual wound is the most important factor determining management, and an understanding of ballistics allows the surgeon to better understand the pathology and assess the injuries that he sees, rather than explain every wound and determine specifc treatment. Internal ballistics Internal ballistics deals with the processes that occur inside a gun barrel when a shot is fred: gas pressures on combustion of the propellant powder, the energy and heat released, and the course of the projectile in the barrel, are just some of its concerns. The infuences afecting the fight include gravity, air resistance and crosswind defection, stability of the projectile (spin and yaw), as well as any contact prior to the projectile reaching the target, known as ricochet. Terminal ballistics Terminal ballistics describes what happens when the projectile hits the target, as Bullet well as any counter-efects produced by the target on the projectile. If the target is Case biological tissues, terminal ballistics is called wound ballistics and describes the efects on the tissues. This causes a very rapid burn with the production of a large volume of rapidly expanding gas, which pushes the bullet out of the barrel of the gun. The velocity with which the bullet leaves the barrel is called the muzzle velocity.
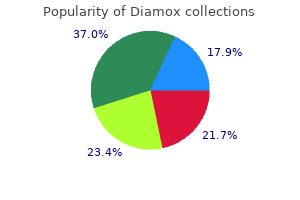
Discount diamox on line
Following implementation of therapy, patients should be reassessed for attainment of treatment goals and identification of any barriers for successful treatment (Figure 4. Initial pharmacological management Rescue short-acting bronchodilators should be prescribed to all patients for immediate symptom relief. Long-acting inhaled bronchodilators are superior to short-acting bronchodilators taken as needed i. Follow-up pharmacological management the follow-up pharmacological treatment algorithm (Figure 4. The need to treat primarily dyspnea/exercise limitation or prevent exacerbations further should be evaluated. If a change in treatment is considered necessary then select the corresponding algorithm for dyspnea (Figure 4. Follow up pharmacological management should be guided by the principles of first review and assess, then adjust if needed: 86 > Review? Any change in treatment requires a subsequent review of the clinical response, including side effects. Dyspnea 13 > For patients with persistent breathlessness or exercise limitation on long acting bronchodilator monotherapy, the use of two bronchodilators is recommended. Inhaler technique and adherence should be considered as causes of inadequate treatment response. The best available evidence exists for the use of azithromycin, especially in those who are not current smokers. This can be considered if there are adverse effects (such as pneumonia) or a reported lack of efficacy. The basis of enabling patients to become active partners in their ongoing care is to build knowledge and skills. It is important to recognize that patient education alone does not itself change behavior 26,27 or even motivate patients, and it has had no impact on improving exercise performance or lung function, but it can 28 play a role in improving skills, ability to cope with illness, and health status. Implicit in this description is the provision of self-management support/coaching, which refers to the strategies, techniques and skills used by healthcare providers to arm patients with the knowledge, confidence and skills required to self-manage their disease effectively. Physical activity Pulmonary rehabilitation, including community and home-based, is an approach with clear evidence of benefits. As such, there has been tremendous interest in 34 implementing behavior-targeted interventions with the aim of improving physical activity and these should be 31 encouraged. Technologybased interventions have the potential to provide convenient and accessible means to enhance exercise self-efficacy, and to educate and motivate people in their efforts to make healthy lifestyle changes. These could relate to each patient at different time points of the disease trajectory. The components of pulmonary rehabilitation may vary but evidence-based best practice for program delivery includes: structured and supervised exercise training, smoking cessation; nutrition counseling; and self-management education. Further details and recommendations on the components of pulmonary rehabilitation, the program organization 28 (duration and structure) and evaluation are presented in Chapter 3.
Best order diamox
Papilloedema due to tumours of the anterior fossa is relatively rare and occurs late in the course of the disease. In general, Choroid those tumours which tend to produce internal hydrocephalus Optic disc are most likely to cause papilloedema. Other intracranial causes include a brain abscess, thrombosis of the cavernous sinus or other intracranial veins, aneurysm, Optic subarachnoid haemorrhage, pseudotumour cerebri and hydronerve cephalus. Central retinal vein Pseudotumour cerebri, previously often termed as beMeningeal sheath nign intracranial hypertension, is a disorder associated with A raised intracranial pressure in the absence of an intracranial space-occupying lesion. It tends to occur in obese females in the second or third decades, producing headache with tranChoroid Increased sient blurring of vision and occasional photopsia. Transient obscurations (blurring) of vision and the presence of opticociliary shunts are bad Swollen Optic prognostic factors for vision. Other risk factors, particularly optic disc nerve in the older age group, are anaemia and high myopia. Episodes of transient attacks and mushrooms out so that the vessels bend sharply over its of blurred vision, or transient obscurations of vision, usumargins. With the indirect method of ophthalmoscopy a ally described as bilateral or monocular black-outs lasting defnite parallax may be elicited between its summit and for a few seconds often precipitated by changes in posture, the retina beneath, and by the direct method a difference of are not uncommon in the initial stages. As the condition 2?6 D may be found between the focus of the vessels at the progresses vision worsens with an enlargement of the blind surface of the disc and those on the retina a little way off. At this stage, relative scotomata, and in the neighbouring retina where they may be both frst to green and red, may be present. Severe loss of that this tissue is thrown into folds, and the veins, now tortucentral visual acuity can occur with chronic papilloedema. Other symptoms include headache, which becomes and becomes opaque, and exudates begin to appear on its worse in a recumbent position or is worst in the early mornsurface and in the retina itself. The radiating, oedematous ing when the patient wakes up, but may improve during the folds around the macula take on the appearance of a macular day. Patients may complain of nausea and vomiting and star, usually incomplete and fan-shaped on the side towards diplopia (double vision) due to non-specifc paresis of the the disc, while fuffy patches (cotton-wool spots due to retinal sixth nerve caused by raised intracranial pressure. At this stage the ophthalmoscopic picture may Signs be indistinguishable from that of malignant hypertension. Signs vary but one of the frst is a blurring of the margins With increasing pressure in the tissue of the swollen of the optic disc. The blurring starts at the upper and lower disc, the vascular supply gets compromised leading to focal margins and extends around the nasal side, while the teminfarcts, ischaemia and direct pressure-induced axonal poral margin is usually still visible and sharp. Frequently, the swelling begins to subside before comes hyperaemic and gradually, progressive oedema exthis fnal stage is reached, but in all cases subsidence eventends over the surface of the disc reducing the size of the tually occurs, a process preceded by atrophic changes when physiological cup, blurring the temporal margin and spreadthe nerve fbres can no longer withstand the pressure and ing into the surrounding retina (Fig. When this process commences, the vascularity swells the veins become congested and turgescent; their of the disc diminishes so that it appears pale grey in colour; pulsations may be absent even on applying pressure on the and eventually, even though the increase in intracranial globe. It is important to note that as venous pulsations are pressure may remain unrelieved, the disc becomes fat and absent in 10?15% of the normal population, this sign in atrophic.
Additional information: