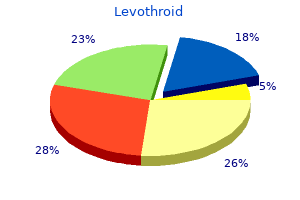
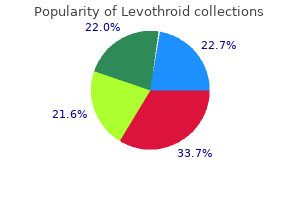
"Levothroid 50mcg generic, thyroid gland function in dogs".
By: D. Gelford, M.A., Ph.D.
Program Director, University of Cincinnati College of Medicine
Cheap levothroid amex
Importance Global importance in terms of effects on wildlife, livestock and humans, and economic importance. Factsheet header explained the factsheet header contains a quick summary of the disease, including the most widely known names of the disease, symbols to indicate which taxa are affected, a brief description of the wetland types in which the disease might be found, and three boxes indicating whether or not the disease can occur in wildlife, livestock and humans, plus the level of impact the disease has on each of these groups. Wildlife Wetlands inhabited by the Livestock tsetse fly Human How the disease affects livestock. The taxa categories are invertebrates, fish, amphibians & reptiles, birds and mammals. The taxa symbols appear in the factsheet headers in two colours: black indicates the taxa that are usually affected, and grey indicates the taxa that can also be affected (see example above). These categories are assigned based on impacts at the global scale rather than impacts on an individual or a population. Notifiable diseases bring trade restrictions and a range of necessary disease control measures. Infection of susceptible cattle results in acute or chronic disease which is characterised by intermittent fever, anaemia, occasional diarrhoea and rapid loss of condition and often terminates in death. Species affected Many species of domestic and wild animals including cattle, swine, camels, goats and sheep. Cattle are prefered by the tsetse fly and this preference can shield other animals from the effects of trypanosomiasis. Wild animals known to be infected but which are trypanotolerant include greater kudu Tragelaphus strepsiceros, warthog Phacochoerus africanus, bushbuck Tragelaphus scriptus, bush pig Potamochoerus porcus, African buffalo Syncerus caffer, African elephant Loxodonta africana, black rhinoceros Diceros bicornis, lion Panthero leo and leopard Panthera pardus. The three main species of tsetse flies responsible for transmission are Glossina morsitans, which favours open woodland on savanna; G. How is the disease Trypanosomes must first develop within tsetse fly vectors for one to a few transmitted to animalsfi Trypanosomes can also be mechanically transmitted by biting flies when these flies transfer blood from one animal to another. Animals imported from endemic areas can be subclinical carriers and may become ill with the disease when stressed.
Purchase generic levothroid canada
Ovale malaria occurs mainly in sub-Saharan Africa where vivax malaria is much less frequent. Non-human primates are naturally infected by some malaria parasite species, which can infect humans experimentally, although natural transmission to humans is rare. Most species feed at night; some important vectors also bite at dusk or in the early morning. In the susceptible host, sporozoites enter hepatocytes and develop into exo-erythrocytic schizonts. When these mature, the infected hepatocytes rupture; asexual parasites reach the bloodstream and invade the erythrocytes to grow and multiply cyclically. At the time of each cycle, rupture of large numbers of erythrocytic schizonts induces clinical symptoms. Within infected erythrocytes, some of the merozoites may develop into male or female forms, gametocytes. Gametocytes usually appear in the blood stream within 3 days of overt parasitaemia with P. This phenomenon does not occur in falciparum or malariae malaria, and reappearance of these forms of the disease (recrudescence) is the result of inadequate treatment or of infection with drug-resistant strains. Injection or transfusion of infected blood or use of contaminated needles and syringes. However, pregnant women are more vulnerable than others to falciparum malaria (and possibly other Plasmodium species). In low transmission areas, pregnant women are at high risk of severe malaria, abortion and premature delivery. With infection through blood transfusion, incubation periods depend on the number of parasites infused and are usually short, but may range up to about 2 months. Suboptimal drug suppression, such as from prophylaxis, may result in prolonged incubation periods.
Cheap levothroid amex. I had half of my thyroid removed through my armpit ~ a thyroid story.
Woodbind (English Ivy). Levothroid.
- Chronic bronchitis.
- What other names is English Ivy known by?
- How does English Ivy work?
- Coughs; spasms; gout; arthritis-like pain; diseases of the liver, spleen, and gallbladder; burns; calluses; nerve pain; and ulcers.
- Are there safety concerns?
- What is English Ivy?
- Dosing considerations for English Ivy.
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96474
Levothroid 50mcg generic
This concept is postulated because the genomic sequences of canine distemper virus, rindepest virus, and measles virus have more in common than do sequences from other types of viruses. Such interrelationships between these three viruses likely occurred at the time when large human populations first lived in close proximity to domestic animals. Thus, whenever a virus encounters an unfamiliar organism, the virus may undergo multiple mutations and emerge as a variant that produces a severe and novel disease. Termed H1, H2, or H3, the hemagglutinin of human infiuenza virus has been replaced by a bird hemagglutinin termed H5 in what we call bird fiu. Infectious for certain birds, H5 bird fiu has now infected humans for the first time, and the resultant mortality is high in humans hospitalized with bird fiu. However, the H5 bird virus that infected humans has not yet undergone significant transmission from one human to others. When or if that happens, then another serious pandemic of infiuenza is likely to occur. To maintain itself in nature and to replicate, a virus must undergo a series of steps. Thereafter, the virus uses its evolved strategies to express its genes, replicate its genome (genes placed in the correct order and orientation), and assemble its component parts (nucleic acids and proteins) in multiple copies or progeny (offspring). Upon completion of this sequence, mature viruses formed during the replication process exit from the infected cell by a process called budding. In some cases the virus, once it has made multiple progeny, will kill the cell as a mechanism for releasing new viruses. Generally, the attachment and entry of viruses into cells are dependent both on the activities of the host cell and on the properties of selected viral genes. The cell has on its surface receptors to which viruses attach and bind with proteins evolved specifically for that purpose. Introduction to the Principles of Virology 13 As described above, the attachment or binding of a viral protein (specifically, an amino acid sequence within that protein) to a cell receptor is the first step that initiates infection of a cell. The unique distribution of certain receptors and either their limitation to a few cell types or, instead, their broad range on many different cell types dictates how many portals of entry exist for a virus. For example, infection/killing of the irreplaceable neuronal cells in the central nervous system or of cells in the heart whose function is essential to life is extremely ominous.
Order levothroid discount
While the rest of this chapter is organized according to these mechanisms (see Table 14. It should be noted that emerging or resurging diseases may occur across many ecosystems even though they have been grouped here according to the major ecosystem in which they are prevalent. Examples of diseases emerging or resurging due to habitat change that occur across many ecosystems are described here for cultiFigure 14. Convergence Model for the Emergence of vated, drylands, forest, urban, and coastal systems. Infectious Diseases, Combining Multiple Causes of Disease Emergence or Reemergence (Institute of Medicine 2003) 14. Mechanisms of Disease Emergence and Examples of Diseases across Ecosystems Mechanisms Ecosystems Cultivated Systems Dryland Systems Forest Systems Urban Systems Coastal Systems Habitat schistomiasis hantavirus malaria lymphatic filariasis cholera alteration Japanese encephalitis Rift Valley fever arboviruses Dengue fever. They serve more purposes than large dams: for example, a Inevitably, this growing trend in water resources development small multipurpose project may provide water for domestic suphas resulted in qualitative and quantitative changes in natural bioplies, fishing, cattle, and irrigation while providing fiood control. Large-scale human resettlement, dams in the world, it is likely that their collective volume is which usually occurs in conjunction with irrigation development, greater than that of large dams. In Nigeria and Zimbabwe, for has resulted in exposure to disease in nonimmune populations. There is usually resources development has often been accompanied by invasions a high degree of water contact with people and animals, so disease of new disease-carrying vectors or population changes in existing transmission rates are high (Hunter et al. However, there vectors, as well as similar changes in disease agents, which have have been relatively few epidemiological studies on disease trends increased the risks of disease (Bradley and Narayan 1988). For instance, intense transmission of diseases of mortality and morbidity due to different diseases. A similar caveat applies Irrigation canals are known to provide ideal habitat for the snails to economic indicators that point to significant impacts. Clinical signs for the two infections are blood in the Human Health: Ecosystem Regulation of Infectious Diseases 399 urine and blood in the stools, respectively. These factors may selectively favor some species and displace highest prevalence along the lower Tana, where the now largely or change the relative dominance of certain species or genotypes. In 1956, when the With malaria, in particular, the result can be marked changes scheme began, there were no snail vectors of S. The varied epidemiology of malaria in different urinary schistosomiasis among local children, which rose to 90% cultivated systems in Africa is aptly reviewed by Ijumba and Lindby 1982 due to poorly maintained irrigation channels. This anomaly has been largely attributed to differences in soThere are many examples worldwide of vector-borne disease cioeconomic and ecological environments inside and outside irriproblems linked to water resources development (see reviews of gation schemes. For instance, villages surrounded by irrigated rice Bradley 1977; Mather and That 1984; Service 1984). The most plausible explanation for this appeared to be increase in the extent of mosquito breeding surface and an inthe tendency of An. Added to this and mosquito-borne disease are from South Asia, and they provide conwas biological disturbance in terms of the replacement of a diverse natural trasting examples of the aggravation of health problems resulting from forest fiora and fauna by the introduction of a virtual crop monoculture irrigation development in a tropical environment (Sri Lanka) and a more (rice), and a dominant large mammal population (humans, often from northern desert region (India).