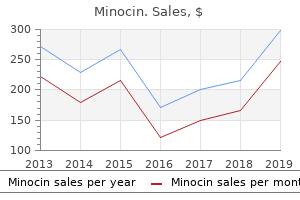
"Buy minocin online now, antimicrobial cleaning products".
By: U. Mortis, M.A., M.D., Ph.D.
Co-Director, Pennsylvania State University College of Medicine
Buy minocin discount
Prenatal diagnosis the approach for prenatal diagnosis of fetal tumors should be based on three sets of ultrasound signs: general signs, organ-specific signs and tumor-specific signs. The general sonographic features, that should raise the suspicion of an underlying fetal tumor, include: (1) Absence or disruption of contour, shape, location, sonographic texture or size, of a normal anatomic structure; (2) Presence of an abnormal structure or abnormal biometry; (3) Abnormality in fetal movement; (4) Polyhydramnios; and (5) Hydrops fetalis. Polyhydramnios is particularly important, because almost 50% of fetal tumors are accompanied by this finding. The underlying mechanisms include interference with swallowing (such as thyroid goiter or myoblastoma), mechanical obstruction (such as gastrointestinal tumors), excessive production of amniotic fluid (such as sacrococcygeal teratoma), and decreased resorption by lung tissue in lung pathology. Intracranial tumors are also commonly associated with polyhydramnios and the mechanism may be neurogenic lack of swallowing or inappropriate polyuria. Tumor-specific signs include pathological changes within the tumor mass (calcifications, liquefaction, organ edema, internal bleeding, neovascularization and rapid changes in size and texture). Organ-specific signs are rare, but in some cases they are highly suggestive of the condition (such as cardiomegaly with a huge solid or cystic mass occupying the entire heart, suggesting intrapericardial teratoma). Examples may vary from severe cases of bladder exstrophy (where the protruding bladder mass appears as a solid tumor-like structure), to rare cases of fetal scrotal inguinal hernia (where bowel loops occupy the scrotum, appearing as huge masses). Prognosis Apart from intracranial tumors (where the prognosis is generally poor), the prognosis for tumors in other locations is variable and depends on the size of the tumor (with resultant compression of adjacent organs), degree of vascularization (with the risk of causing heart failure and hydrops), and associated polyhydramnios (with the risk of preterm delivery). Prevalence Brain tumors are exceedingly rare in children, and only about 5% arise during fetal life; teratoma is the most frequently reported. Etiology Embryonic tumors are thought to derive from embryologically displaced cells. Brain tumors have been produced in animals by the use of chemical and viral teratogens. Diagnosis A brain tumor should be suspected in the presence of mass-occupying lesions (cystic or solid areas), and a change in shape or size of the normal anatomic structures (such as shift in the mid-line). Cystic tumors and teratomas are usually characterized by complete loss of the normal intracranial architecture. In some cases, the lesion appears as a low echogenic structure, and it may be difficult to recognize. Hydrocephalus is frequently associated with brain tumors and may be the presenting sign. The ultrasound appearances of all intracranial tumors are similar and, therefore, precise histological diagnosis from a scan is almost impossible. Possible exceptions are lipomas (that have a typical hyperechogenic homogeneous appearance) and choroid plexus papillomas (that appear as an overgrowth of the choroid plexus).
Buy minocin online now
The tumour is well-circumscribed, dark-tan and covered by a thin shell of subperiosteal bone. Grossly, chondrosarcoma Cut surface of the tumour is characteristically haemormay vary in size from a few centimeters to extremely large rhagic, necrotic, and honey-combed due to focal areas of and lobulated masses of firm consistency. These tumour cells show cytologic features Giant cells often contain as many as 100 benign nuclei of malignancy such as hyperchromatism, pleomorphism, and have many similarities to normal osteoclasts. These two or more cells in the lacunae and tumour giant cells cells have very high acid phosphatase activity. Histologic features include invasion of the tumour into adjacent soft tissues and cytologic characteristics of malignancy in the tumour cells. Sectioned surface shows circumscribed, dark tan, haemorrhagic and necrotic tumour. Though designated as giant cell tumour Stromal cells are mononuclear cells and are the real tumour cells and their histologic appearance determines or osteoclastoma, the true tumour cells are round to spindled the biologic behaviour of the tumour. Available evidence suggests that osteoclasts are derived from fusion of circulating monocytes, Other features of the stroma include its scanty collagen content, rich vascularity, areas of haemorrhages and the process being facilitated by transforming growth factorpresence of macrophages. These are: its cell of origin, its are present in several other benign tumours and tumourdifferentiation from other giant cell lesions and its biologic like lesions from which the giant cell tumour is to be behaviour. Microscopy reveals osteoclast-like multinucleate giant cells which are regularly distributed among the mononuclear stromal cells. The common sites are Approximately 4% cases result in distant metastases, mainly shafts and metaphysis of long bones, particularly femur, tibia, to lungs. Metastases are histologically benign and there is humerus and fibula, although some flat bones such as pelvis usually history of repeated curettages and recurrences. These signs and symptoms may lead to an tumour is the role of radiotherapy resulting in development erroneous clinical diagnosis of osteomyelitis. However, Xof post-radiation bone sarcoma though primary (de novo) ray examination reveals a predominantly osteolytic lesion malignant or dedifferentiated giant cell tumour may also with patchy subperiosteal reactive bone formation producing occur. Since its tissue is characteristically grey-white, soft and friable first description by James Ewing in 1921, histogenesis of this (Fig. Characteristic microscopic features are irregular lobules of uniform small tumour cells with indistinct cytoplasmic outlines which are separated by fibrous tissue septa having rich vascularity.
Cheap minocin 50 mg with visa
The amorphous material is intractable, severe, itching, burning, pruritic an example of rash of the hands and lower extremities that (A) apocrine metaplasia. A 49-year-old man has a recent diagnosis His father, paternal uncle, and several of small cell carcinoma of the lung. Which of other family members have similar the following is an important characteristic abnormalities. A 45-year-old man presents with a form transfusions, he died during an emergency of bacterial infection in which the invadlaparotomy that revealed a ruptured spleen ing microorganisms are opsonized prior and a slightly enlarged liver. Of examination of the liver at autopsy revealed the following complement components or intracytoplasmic clear vacuoles displacing groups of components, which is most likely the intact nuclei of the hepatocytes to the involvedfi Special stains will (A) C3a and C5a most likely demonstrate that the vacuolar (B) C3b material is (C) C4a (A) bilirubin. A 5-year-old boy is seen because he continuous through the years, there have has recurrent hemarthroses and a large been episodic exacerbations of these symppainful hematoma involving the soft tissues toms, which have worsened during the of his right thigh. Given the following past 4 or 5 years, lasting 3 or 4 months at choices, which is the most likely cause of the a time. A 43-year-old woman has a recent (C) Lung carcinoma diagnosis of Hashimoto thyroiditis. This scenario suggests which of (D) Presence of Hurthle cells the following disordersfi An autopsy is performed on a (C) Pseudomembranous colitis 60-year-old man with a history of sustained (D) Ulcerative colitis ethanol abuse. There had been a history (E) Whipple disease of progressive dementia with marked memory loss manifested by a tendency to 63. On admission to the hospital, his brain are skin was cold and clammy, his pulse was (A) amyloid-containing neuritic plaques rapid and thready, and his blood pressure within cerebral cortex, amygdala, and was 60 systolic and 40 diastolic. A 4-year-old girl has had multiple hospi(A) finely granular renal surface and talizations for pneumonia. Additionally, she hyaline arteriolosclerosis of afferent is small for her age and has had symptoms arterioles. Chest radiograph (C) nodular mesangial accumulations of demonstrates pulmonary infiltrates indicabasement membrane-like material and tive of pneumonia. Which of the following is hyaline arteriolosclerosis of afferent and the most likely pathogen causing pulmonary efferent arterioles. The most likely diagnosis in a 24-yearfusion for profuse bleeding associated with old woman with the nephrotic syndrome, a complication of childbirth. Shortly thereprogressive azotemia, and thickening of after, she had an acute disease diagnosed glomerular capillary loops apparent on light as non-A, non-B hepatitis.
Order minocin with a mastercard
Early on all that is needed to take care of symptoms is the use of support stockings. Your doctor will be able to tell you if this is the problem and, if so, if other treatment will be needed. My child has a congenital venous malformation, are we at risk for other children with the same problemfi Most congenital venous malformations do not run in the family, in other words, are not genetically determined. You would have to discuss this with your doctor to know for sure if this is a concern for your family. See pages 26 (Getting Started), 27 (Diagnosis), 28 (Treatment Response), 29 (Technique), 30 (Management), 31 (Reporting), 32 (Imaging Features). Measure Viable Tumor Size How to measure thick irregular How to measure nodular Size of equivocally, probably, or viable tumor viable tumor definitely viable tumor Longest dimension through enhancing area of treated lesion, Nonenhancing Nonenhancing not traversing nonenhancing area area area Enhancing Largest area enhancing area Step 3. Radiologists are encouraged to use their judgment and tailor the recommendations to each patient. If an observation has been biopsied and there is no uncertainty about the path diagnosis. Rationale: reporting both may alert referrer to possible false-negative biopsy results and/or need for close follow-up to detect progression. Enhancing part must be higher in attenuation or intensity than liver in arterial phase. Likely reflects peripheral hypercellularity and central stromal fibrosis or ischemia. Radiologic viability is not synonymous with pathologic viability as imaging is not sensitive to microscopic or small foci of residual tumor. Treatment-specific expected Expected temporal and spatial pattern of posttreatment enhancement enhancement attributable to treatment-related changes in parenchymal perfusion. For some treatments, early posttreatment enhancement patterns may not reliably differentiate viable from nonviable tumor. No lesional enhancement Absence of enhancement within or along the margin of a treated lesion.
Buy minocin discount. Superbugs: CDC's 2013 List of the Biggest Drug-Resistant Threats.