"Buy tamsulosin toronto, mens health 82 day speed shred".
By: C. Curtis, M.A.S., M.D.
Clinical Director, Tulane University School of Medicine
Safe tamsulosin 0.2 mg
In contrast, knowledge in areas of technology and science generally is growing rapidly. As we will see, this knowledge is often quite at odds with the conventional wisdom of ed ucation. The scientifc understanding of the human brain, and how it works, is beginning to show that learning is not an abstract transmission of knowledge to an infnitely plastic intelligence but a biochemical process with physical limitations. Stu dents could learn by holding conversations in natural language, such as in the 74 AutoTutor system developed by Art Graesser and colleagues and in virtu al reality environments, such as Crystal Islands developed by James Lester and colleagues and the Tactical Language and Culture System developed by75 Lewis Johnson. These systems promoted constructivism and collaboration,76 with engaging social and emotion sensitive interaction. Desire for increased, evidence-based rigor was also seen among assessments 77 of learning. Relatedly, by the end of this decade, increasing com puting power and the expanding amounts of learning data encouraged the de 80 velopment of learning analytics, led by George Siemens and his colleagues, and educational data mining, led by Ryan Baker and his colleagues. Although research ers continue to debate the fner points of these defnitions, both felds emphasize the use of measurement, collection, and An early AutoTutor interface from the 1990s, courtesy of Graesser et al. However, a few trends already stand out for our current decade, but whether they will stand the test of time remains to be seen. We traced the funding investments from the 1970s until now and noted that the funding is coming from different places, including multiple federal agencies and private foundations. Both the content-agnostic and content-dependent ap proaches have been funded in parallel over the years, and both have made important contributions to our understand ing of how people learn. You need the content agnostic ap proach to identify promising learning principles but the con tent dependent is also necessary because each content area has unique needs. Department of Education Look for Higgins, Dettmer, and Albro, currently in press History of Distributed Learning | 37 access and large scale. These platforms, which attempt to provide learning at scale, have been signifcantly aided by the development of cloud computing in the 2000s and by the con sumer release of Amazon Web Services and Microsoft Azure. Cloud computing also helped realize the Internet of Things (IoT), the network of smart devices that can connect to networks and share data.
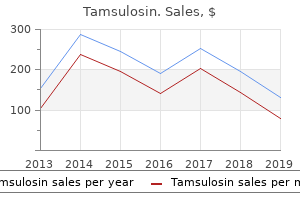
Buy tamsulosin no prescription
In other words, it will not be possible to obtain feedback on paper drafts submitted after the date specified above. Any plagiarism on written assignments will be associated with a failing grade on the assignment, possibly in the class, and serious disciplinary action. Reading: Powers Behavioral Assessment of Individuals with Autism (Chapter 28: Handbook of th Autism: 4 edition, pp. Neural mechanisms of improvements in social motivation after pivotal response treatment: two case studies. A Review of the Research to Identify the Most Effective Models of Practice in Early Intervention for Children with Autism Spectrum Disorders. A, Review of the Research to Identify the Most Effective Models of Practice in Early Intervention for Children with Autism Spectrum Disorders, (2006) Australian Government Department of Health and Ageing. The authors would like to acknowledge the contribution of the advisory group for this review: Dr Natalie Silove, Professor Valsamma Eapen, Dr Angelika Anderson and Mrs Judy Brewer Fischer. Disclaimer the Commonwealth of Australia accepts no responsibility for the accuracy or completeness of any material contained in this report. Additionally, the Commonwealth disclaims all liability to any person in respect of anything, and the consequences of anything, done or omitted to be done by any such person in reliance, whether wholly or partially, upon any information contained in this report. Any views and recommendations of third parties contained in this report do not necessarily reflect the views of the Commonwealth, or indicate a commitment to a particular course of action. Australian Government Department of Families, Housing, Community Services and Indigenous Affairs, Australia. Processes for regularly updating information about evidence of effectiveness and best practice. This report reviews the latest research evidence, and includes a discussion of what is currently understood about principles of good practice in autism early intervention, and the application of those principles in practice. Evidence-based treatment guidelines are particularly important in the field of autism where there has been considerable controversy surrounding the effectiveness of various treatments, including those which are well promoted but lack scientific evidence for their perceived effectiveness. Although some of these interventions might be helpful to children, others might be ineffective or even harmful. Research evidence is needed to address these claims and also to prevent limited resources from being invested in non-productive programs. Previous syntheses of evidence have found that only a small number of autism treatment programs have direct research evidence that supports their effectiveness, and that this research is limited. In other words, previous reviews have found that very few outcomes of particular autism interventions are sufficiently robust to allow confident recommendations about their efficacy or otherwise. Most treatments have not been evaluated adequately and many have not been evaluated at all. In the absence of direct evidence, parents and professionals must also consider how well an intervention meets guidelines for good practice in autism intervention and the extent to which the rationale for the intervention is based on research evidence about autism.
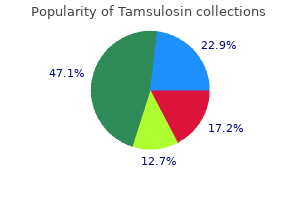
Buy tamsulosin toronto
Flexibility and Inclusion To ensure that all students are provided opportunities for real learning experiences, flexibility and options should be built into the planning of teaching strategies, materials, and student activities. For example, a student who has difficulty with concepts in mathematics may be motivated to learn graphing techniques by gathering data on items of personal or special interest. They often require flexibility regarding the timing the learning opportunities and method used to demonstrate their knowledge and skills. The classroom is filled with many sensory demands that can be overwhelming for some students. For example, tennis balls can be used to cover the bottoms of chair legs to reduce classroom noise. Simplicity Teachers should ensure that the information provided in learning situations is presented clearly and is easily understood by the students. Unnecessarily complex and distracting information should be reduced as much as possible. They will often have difficulty understanding complex, abstract language and may misinterpret metaphors, slang terms, and colloquialisms. Effective methods to simplify information and make it easier for the student to understand include using clear and concise language, breaking instructions and tasks into smaller steps, and using visual supports, such as written or picture schedules. Information and materials should be organized in such a way that important or key components are highlighted and easily identified by students. A safety assessment can help to identify the factors that may lead to or cause situations and provide an assessment of the potential risks in given situations. A safety plan outlines the appropriate responses and supports that are required during specific situations with students. Suggestions to Support activities and settings within the routines of the school day. Preparing Students for Other transitions, such as class excursions, occur less frequently. Planning for transitions provides the foundations for successful transition experiences that help a student learn to cope with change and adapt to a variety of settings. The planning can be complex and requires communication and coordination between those who will be involved in the transition process. Effective planning for significant transitions usually includes parents and staff from the school, school board, and community agencies who are and who will be involved with the student. They can also help to support successful See Chapter 4: transitions by assisting in determining an effective transition 23.
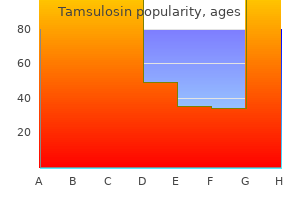
Order genuine tamsulosin
With regard to parent training paradigms to address challenging behavior, results of parent training studies and parent training in addition to 90 treatment with risperidone have demonstrated short-term improvements in terms of the frequency and intensity of challenging behavior. With few higher quality studies in this area, we considered the strength of the evidence to be insufficient (Table 17). The clinical implications of changes in brainwave patterns reported in the studies are unclear, and the studies were small and short 192, 194, 195 term. One poor quality study of 191 parent education to mitigate feeding problems reported no significant effects. Table 17 outlines interventions/outcomes for which we considered the strength of the evidence to be insufficient. Modifiers of Treatment Effects Understanding the degree to which child characteristics. However, as was reported in the 2011 review, few studies were clearly designed or powered to allow for analysis of heterogeneous effects. Primarily studies in this section are those in which potential correlates were identified that may be moderators, but have not been studied as such. Higher cognitive skills and higher adaptive behavior scores at baseline also were often associated with better outcomes across behavioral interventions, but the associations were not consistent. Regarding intervention-related factors, duration of treatment had an inconsistent effect, with some studies reporting improved outcomes with greater intervention time and others reporting no association. Studies have often not been adequately designed or controlled in order to help identify true moderators of treatment. Treatment Phase Changes That Predict Outcomes the reviewed literature offers little information about what specific early changes from baseline measurements of child characteristics might predict long-term outcome and response. Some evidence suggests that the best predictor of long-term outcome is not baseline characteristics at all, but rather the magnitude of change seen over the course of treatment. Treatment Effects That Predict Long-Term Outcomes Few studies assess end-of-treatment effects that may predict outcomes. Several early intensive behavioral and developmental intervention paradigms change measures over the course of very lengthy treatments, but such outcomes usually have not been assessed beyond treatment 140, 141, 148, 149 windows. It also involved children were receiving many hours of uncontrolled interventions during the course of study. Generalization of Treatment Effects Few studies included in this review explicitly measured generalization of treatment effects to different conditions or locations. Presumably, changes measured on these instruments document important skills with potential impact in other areas. However, some caution is warranted: In some instances, the interventions themselves may actually target component skills of these assessments, particularly in the case of cognitive and language assessments.
Order cheapest tamsulosin and tamsulosin
For instance, teachers and trainers can provide scaffolds to help guide learners through these self-directed learning processes. In closing, this section has offered the barest summary of instructional theories. Harold Pashler and colleagues published seven principles for instructional strategies, including recommendations for spaced learning, using worked examples in combination with problem solving, combining graphic and verbal descriptions, integrating abstract and concrete concepts, using quizzing and questions to eliminate misconceptions, and supporting self-regulated learning by helping learners 50 | Modernizing Learning 12 allocate study time. Art Graesser built on prior work to defne 25 principles of learning (clearly an overachiever in learning frameworks! Finally, for a truly comprehensive historic treatment, Peter Jarvis authored a three-volume set, beginning with the book, Towards a Comprehensive Theory of Human Learning. Starting in the around the 1960s, researchers be gan to also examine learner-interface dynamics, leading to unique pedagogies for educational technology. Early work on instructional media involved com parison studies, often looking at technology-mediated versus traditional set tings. In the 1980s, with growing interest in the cognitive perspective, researchers began to look more closely at media attributes and their interactions with individual differences. Recommendations for technology-enabled instruction naturally followed from these tenets. For example, given the limits of working memory, multimedia learning materials need to moderate the amount of essential processing re quired by the learners depending upon their prior knowledge, experience, and competencies. Many other design principles can also be derived; these cluster under 12 principles, as summarized in the adjacent graphic. This model helps explain why, for instance, the frst web-course designers attempted to recreate printed texts online or why the original virtual classrooms took so many cues from physical ones. The most basic, and most often implemented level is substitution, where the Distributed Learning Instructional Theories | 53 technology is used to perform the same task as was done before. For example, an instructor uses PowerPoint to replace acetate slides or students use laptops to replace paper notebooks. Alternatively, the highest level is redefnition, where technology supports new learning tasks that were previously incon ceivable.
Safe tamsulosin 0.2 mg. Should you take vitamins?.